Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales in the Western Balkans: Addressing Gaps in European AMR Surveillance Map
- PMID: 39335068
- PMCID: PMC11428970
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics13090895
Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales in the Western Balkans: Addressing Gaps in European AMR Surveillance Map
Abstract
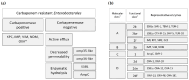
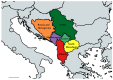
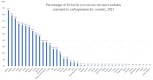
In the context of global efforts to combat antimicrobial resistance (AMR), the importance of comprehensive AMR data is more crucial than ever. AMR surveillance networks, such as the European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network (EARS-Net) and the Central Asian and European Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance (CAESAR), support member states in obtaining high-quality AMR data. Nevertheless, data gaps persist in some countries, including those in the Western Balkans (WBs), a region with high AMR rates. This review analyzed existing research on carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales (CRE) to better understand the AMR landscape in the WB countries. The most prevalent CRE was Klebsiella pneumoniae, followed by Escherichia coli, Enterobacter cloacae, and Proteus mirabilis, with sporadic cases of Morganella morganii, Providencia spp., Klebsiella oxytoca, and Citrobacter sedlakii. Carbapenemase production was identified as the most common mechanism of carbapenem resistance, but other resistance mechanisms were not investigated. An increasing trend in carbapenem resistance has been observed over the last decade, alongside a shift in carbapenemase epidemiology from the NDM type in 2013-2014 to the OXA-48 type in recent years. Few studies have applied whole-genome sequencing for CRE analysis, which has demonstrated the spread of resistance determinants across different niches and over time, emphasizing the importance of molecular-based research. The overall low number of studies in the WB countries can be attributed to limited resources, highlighting the need for enhanced support in education, training, technology, and equipment to improve data collection and evaluation.
Keywords: Western Balkans (WBs); antimicrobial resistance (AMR) data; carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales (CRE).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- O’Neill J. Tackling Drug-Resistant Infections Globally: Final Report and Recommendations. Review on Antimicrobial Resistance; Wellcome Trust; London, UK: 2016.
-
- World Health Organization Global Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance. 2015. [(accessed on 9 April 2024)]. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/193736. - PubMed
-
- WHO . WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List, 2024: Bacterial Pathogens of Public Health Importance to Guide Research, Development and Strategies to Prevent and Control Antimicrobial Resistance. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2024.
-
- Zhou R., Fang X., Zhang J., Zheng X., Shangguan S., Chen S., Shen Y., Liu Z., Li J., Zhang R., et al. Impact of carbapenem resistance on mortality in patients infected with Enterobacteriaceae: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 2021;11:e054971. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-054971. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

