Comparing the Outcomes of Cefoperazone/Sulbactam-Based and Non-Cefoperazone/Sulbactam-Based Therapeutic Regimens in Patients with Multiresistant Acinetobacter baumannii Infections-A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 39335080
- PMCID: PMC11428705
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics13090907
Comparing the Outcomes of Cefoperazone/Sulbactam-Based and Non-Cefoperazone/Sulbactam-Based Therapeutic Regimens in Patients with Multiresistant Acinetobacter baumannii Infections-A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
The addition of sulbactam restores the complete range of cefoperazone activity against bacteria and extends its spectrum of action to include the Acinetobacter species. The effectiveness of cefoperazone/sulbactam against multiresistant Acinetobacter baumannii has not been investigated. The purpose of the current meta-analysis was to compare the efficacy of cefoperazone/sulbactam-based therapeutic regimens and non-cefoperazone/sulbactam-based therapeutic regimens in the treatment of multiresistant Acinetobacter baumannii infections. The current meta-analysis of 10 retrospective studies provides evidence that cefoperazone/sulbactam-based therapeutic regimens are superior to non-cefoperazone/sulbactam-based therapeutic regimens in terms of 30-day mortality and clinical improvement in patients with multiresistant Acinetobacter baumannii infections. The risk of mortality was reduced by 38% among multiresistant Acinetobacter baumannii infections in patients who received cefoperazone/sulbactam-based therapeutic regimens. The cefoperazone/sulbactam-based combination therapy was superior to the cefoperazone/sulbactam monotherapy in terms of 30-day mortality when both therapeutic regimens were compared to the tigecycline monotherapy in patients with multiresistant Acinetobacter baumannii infections.
Keywords: Acinetobacter baumannii; cefoperazone; mortality; multiresistant; sulbactam.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
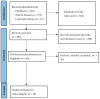
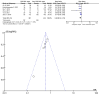
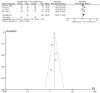
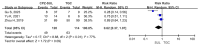
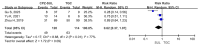
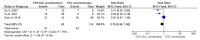
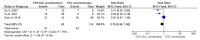
References
-
- Gales A.C., Castanheira M., Jones R.N., Sader H.S. Antimicrobial resistance among Gram-negative bacilli isolated from Latin America: Results from SENTRY Antimicrobial Surveillance Program (Latin America, 2008–2010) Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012;73:354–360. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2012.04.007. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hu F.P., Guo Y., Zhu D.M., Wang F., Jiang X.F., Xu Y.C., Zhang X.J., Zhang C.X., Ji P., Xie Y., et al. Resistance trends among clinical isolates in China reported from CHINET surveillance of bacterial resistance, 2005–2014. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016;22((Suppl. S1)):S9–S14. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2016.01.001. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

