Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy with Concurrent Letrozole for Estrogen Receptor-Positive and HER2-Negative Breast Cancer: An Open-Label, Single-Center, Nonrandomized Phase II Study (NeoCHAI)
- PMID: 39335094
- PMCID: PMC11430478
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16183122
Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy with Concurrent Letrozole for Estrogen Receptor-Positive and HER2-Negative Breast Cancer: An Open-Label, Single-Center, Nonrandomized Phase II Study (NeoCHAI)
Abstract
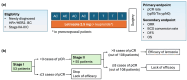
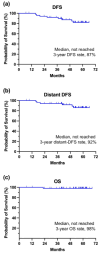
The role of combining neoadjuvant endocrine therapy with conventional chemotherapy remains unclear; therefore, we conducted an open-label, single-center, nonrandomized phase II trial to assess the effect of this combination. Patients with previously untreated stage II or III HR-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer received concurrent letrozole 2.5 mg with standard neoadjuvant chemotherapy. The primary endpoint was pathologic complete response (pCR) at the time of surgery. We used Simon's minimax two-stage design; a pCR rate > 6% was necessary at the first stage to continue. Between November 2017 and November 2020, 53 women were enrolled in the first stage of the trial. Their median age was 49 years (range, 33-63), and 60% of them were premenopausal. Subsequently, 66% and 34% of patients with clinical stages II and III, respectively, were included; 93% had clinically node-positive disease. Two patients (4%) achieved pCR after neoadjuvant chemo-endocrine treatment, which did not satisfy the criteria for continuing to the second stage. The overall response rate was 83%. During the median follow-up of 53.7 months, the 3-year disease-free survival and overall survival rates were 87% and 98%, respectively. Neutropenia was the most common grade 3/4 adverse event (40%), but rarely led to febrile neutropenic episodes (4%). Myalgia (32%), nausea (19%), constipation (17%), heartburn (11%), oral mucositis (9%), and sensory neuropathy (9%) were frequently observed, but classified as grade 1 or 2. No deaths occurred during preoperative treatment. The addition of letrozole to standard neoadjuvant chemotherapy was safe and beneficial in terms of overall response rate, but did not provide a higher pCR rate in locally advanced HR-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer. Further research is needed to enhance neoadjuvant treatment strategies for this cancer subtype.
Keywords: chemotherapy; early breast cancer; endocrine therapy; hormone-receptor positive breast cancer; neoadjuvant treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cortazar P., Zhang L., Untch M., Mehta K., Costantino J.P., Wolmark N., Bonnefoi H., Cameron D., Gianni L., Valagussa P., et al. Pathological complete response and long-term clinical benefit in breast cancer: The CTNeoBC pooled analysis. Lancet. 2014;384:164–172. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62422-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network Guidelines. Breast Cancer (Version 2, 2024) [(accessed on 12 April 2024)]. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/breast.pdf.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous