Enhancing Predictive Accuracy for Recurrence-Free Survival in Head and Neck Tumor: A Comparative Study of Weighted Fusion Radiomic Analysis
- PMID: 39335718
- PMCID: PMC11431645
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14182038
Enhancing Predictive Accuracy for Recurrence-Free Survival in Head and Neck Tumor: A Comparative Study of Weighted Fusion Radiomic Analysis
Abstract
Despite advancements in oncology, predicting recurrence-free survival (RFS) in head and neck (H&N) cancer remains challenging due to the heterogeneity of tumor biology and treatment responses. This study aims to address the research gap in the prognostic efficacy of traditional clinical predictors versus advanced radiomics features and to explore the potential of weighted fusion techniques for enhancing RFS prediction. We utilized clinical data, radiomic features from CT and PET scans, and various weighted fusion algorithms to stratify patients into low- and high-risk groups for RFS. The predictive performance of each model was evaluated using Kaplan-Meier survival analysis, and the significance of differences in RFS rates was assessed using confidence interval (CI) tests. The weighted fusion model with a 90% emphasis on PET features significantly outperformed individual modalities, yielding the highest C-index. Additionally, the incorporation of contextual information by varying peritumoral radii did not substantially improve prediction accuracy. While the clinical model and the radiomics model, individually, did not achieve statistical significance in survival differentiation, the combined feature set showed improved performance. The integration of radiomic features with clinical data through weighted fusion algorithms enhances the predictive accuracy of RFS outcomes in head and neck cancer. Our findings suggest that the utilization of multi-modal data helps in developing more reliable predictive models and underscore the potential of PET imaging in refining prognostic assessments. This study propels the discussion forward, indicating a pivotal step toward the adoption of precision medicine in cancer care.
Keywords: head and neck cancer; predictive modeling; radiomics; recurrence-free survival; weighted fusion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
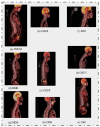



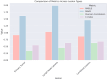

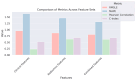
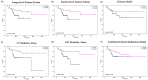
Similar articles
-
Outcome prediction of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by MRI radiomic signatures.Eur Radiol. 2020 Nov;30(11):6311-6321. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-06962-y. Epub 2020 Jun 4. Eur Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32500196 Free PMC article.
-
Fusion-based tensor radiomics using reproducible features: Application to survival prediction in head and neck cancer.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2023 Oct;240:107714. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2023.107714. Epub 2023 Jul 8. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2023. PMID: 37473589
-
Multi-Level Multi-Modality Fusion Radiomics: Application to PET and CT Imaging for Prognostication of Head and Neck Cancer.IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2020 Aug;24(8):2268-2277. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2019.2956354. Epub 2019 Dec 4. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2020. PMID: 31804945
-
Multi-level multi-modality (PET and CT) fusion radiomics: prognostic modeling for non-small cell lung carcinoma.Phys Med Biol. 2021 Oct 14;66(20). doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/ac287d. Phys Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 34544053
-
Radiomic and Clinical Model in the Prognostic Evaluation of Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of the Head and Neck.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Nov 23;16(23):3926. doi: 10.3390/cancers16233926. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39682115 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jayawickrama S.M., Ranaweera P.M., Pradeep R.G.G.R., Jayasinghe Y.A., Senevirathna K., Hilmi A.J., Rajapakse R.M.G., Kanmodi K.K., Jayasinghe R.D. Developments and future prospects of personalized medicine in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma diagnoses and treatments. Cancer Rep. 2024;7:e2045. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.2045. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Trotter J., Pantel A.R., Teo B.K.K., Escorcia F.E., Li T., Pryma D.A., Taunk N.K. Positron emission tomography (PET)/computed tomography (CT) imaging in radiation therapy treatment planning: A review of PET imaging tracers and methods to incorporate PET/CT. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2023;8:101212. doi: 10.1016/j.adro.2023.101212. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

