Pulsed Light Treatment Effect on Color, Oxidative Stability, and Listeria monocytogenes Population of Sliced Mortadella
- PMID: 39335904
- PMCID: PMC11431120
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13182976
Pulsed Light Treatment Effect on Color, Oxidative Stability, and Listeria monocytogenes Population of Sliced Mortadella
Abstract
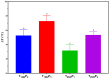
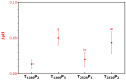
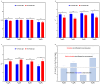
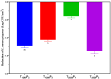
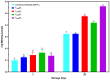
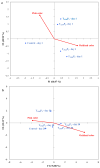
This study evaluated the effects of high-intensity pulsed light (PL) on sliced mortadella, assessing how the parameters pulse width (1260 to 2520 µs) and number of pulses (one to three) influence color, oxidative stability, and Listeria monocytogenes population. The different PL parameters generated a fluence ranging from 2.64 to 6.57 J/cm2 and irradiance ranging from 1046.9 to 1738.8 W/cm2. The PL slightly increased the temperature and pH of the samples, and this elevation was well correlated to the higher number of pulses and higher fluence. The color parameter a* was reduced while b* values increased after PL application, with these effects being more significant in treatments with a higher number of pulses and higher fluence. The highest values of TBARS were found in treatments with higher fluence (5.28 and 6.57 J/cm2), which were characterized by the attribute "oxidized color" in sensory evaluation. The different PL conditions reduced the count of L. monocytogenes by up to 1.44 Log CFU/cm2. The treatment with a pulse width of 1260 µs, two pulses, fluence of 4.38 J/cm2, and irradiance of 1738.3 W/cm2 achieved the same efficacy in pathogen reduction as the treatments with higher fluence. Moreover, these PL conditions had a minimal impact on the color and oxidative stability of mortadella, demonstrating an effective balance between microbiological safety and quality preservation.
Keywords: emulsified meat products; lipid oxidation; non-thermal treatment; post-cooking contamination; sensory profile.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Campagnol P.C.B., Lorenzo J.M., Da Rosa J.L., Dos Santos B.A., Cichoski A.J. Pork: Meat Quality and Processed Meat Products. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2021. Bologna Sausages: Manufacturing Process, Physico-Chemical Composition, and Shelf Life.
-
- Conrad A.R., Tubach S., Cantu V., Webb L.M., Stroika S., Moris S., Davis M., Hunt D.C., Bradley K.K., Kucerova Z., et al. Listeria monocytogenes Illness and Deaths Associated with Ongoing Contamination of a Multiregional Brand of Ice Cream Products, United States, 2010–2015. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023;76:89–95. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciac550. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lachmann R., Halbedel S., Lüth S., Holzer A., Adler M., Pietzka A., Al Dahouk S., Stark K., Flieger A., Kleta S., et al. Invasive Listeriosis Outbreaks and Salmon Products: A Genomic, Epidemiological Study. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022;11:1308–1315. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2022.2063075. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

