A Novel Approach Based on Real-Time PCR with High-Resolution Melting Analysis for the Simultaneous Identification of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus argenteus
- PMID: 39335932
- PMCID: PMC11431256
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13183004
A Novel Approach Based on Real-Time PCR with High-Resolution Melting Analysis for the Simultaneous Identification of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus argenteus
Abstract
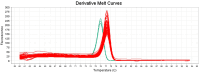
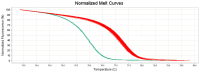
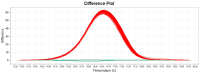
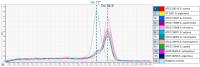
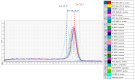
Staphylococcus (S.) aureus is a pathogenic bacterium able to cause several diseases in humans and animals as well as foodborne intoxications. S. argenteus, being phenotypically and genotypically related to S. aureus, is part of the so-called S. aureus complex and recently recognized as an emerging pathogen able to cause, like S. aureus, several diseases both in humans and animals, and foodborne poisoning outbreaks. However, it has been reported that the widely used conventional PCR of Brakstad et al. [Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 30(7), 1654-1660, (1992)] targeting the thermostable nuclease gene may provide false-positive S. aureus, as it is able to amplify also S. argenteus. Here, we developed a novel two-step approach that, following the PCR of Brakstad et al. (1992), discriminates S. aureus from S. argenteus by a real-time PCR with high-resolution melting analysis (rt-PCR-HRM). In particular, targeting a polymorphic 137 bp region of the sodA gene, our developed rt-PCR-HRM method clearly discriminated S. aureus from S. argenteus, showing a remarkable difference in their amplification product melting temperatures (approximately 1.3 °C) as well as distinct melting curve shapes. The good sensitivity, reproducibility, user friendliness, and cost effectiveness of the developed method are advantageous attributes that will allow not only its easy employment to correctly identify misidentified isolates present in various collections of S. aureus, but also expand the still lacking knowledge on the prevalence and distribution of S. argenteus.
Keywords: HRM; Staphylococcus argenteus; Staphylococcus aureus; Staphylococcus aureus complex; high-resolution melting; real-time PCR; sodA gene; species-specific PCR; superoxide dismutase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Licitra G. Etymologia: Staphylococcus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013;19:1553. doi: 10.3201/eid1909.ET1909. - DOI
-
- Fusco V., Quero G.M., Morea M., Blaiotta G., Visconti A. Rapid and reliable identification of Staphylococcus aureus harbouring the enterotoxin gene cluster (egc) and quantitative detection in raw milk by real time PCR. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011;144:528–537. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2010.11.016. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dicks J., Turnbull J.D., Russell J., Parkhill J., Alexander S. Genome sequencing of a historic Staphylococcus aureus collection reveals new enterotoxin genes and sheds light on the evolution and genomic organization of this key virulence gene family. J. Bacteriol. 2021;203:e00587-20. doi: 10.1128/JB.00587-20. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

