Transcriptome-Wide Evaluation Characterization of microRNAs and Assessment of Their Functional Roles as Regulators of Diapause in Ostrinia furnacalis Larvae (Lepidoptera: Crambidae)
- PMID: 39336670
- PMCID: PMC11432511
- DOI: 10.3390/insects15090702
Transcriptome-Wide Evaluation Characterization of microRNAs and Assessment of Their Functional Roles as Regulators of Diapause in Ostrinia furnacalis Larvae (Lepidoptera: Crambidae)
Abstract
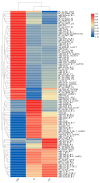
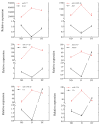
microRNAs (miRNAs) function as vital regulators of diapause in insects through their ability to post-transcriptionally suppress target gene expression. In this study, the miRNA of Ostrinia furnacalis, an economically important global crop pest species, was characterized. For the included analyses, 9 small RNA libraries were constructed using O. furnacalis larvae in different diapause states (non-diapause, ND; diapause, D; diapause-termination, DT). The results identified 583 total miRNAs, of which 256 had previously been identified, whereas 327 were novel. Furthermore, comparison analysis revealed that 119 and 27 miRNAs were differentially expressed in the D vs. ND and DT vs. D, respectively. Moreover, the expression patterns of their miRNAs were also analyzed. GO and KEGG analysis of the target genes of differentially expressed miRNAs highlighted the importance of these miRNAs as diapause regulators in O. furnacalis, especially through metabolic processes, endocrine processes, 20-hydroxyecdysone, and circadian clock signaling pathways. In summary, this study highlighted the involvement of specific miRNAs in the control of diapause in O. furnacalis. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to identify miRNA expression patterns in O. furnacalis, thereby providing reference and novel evidence enhancing our current understanding of how small RNAs influence insect diapause.
Keywords: Ostrinia furnacalis; diapause; miRNA; molecular mechanism; regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competitive economic conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

