Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Generation of Absence Seizures: Identification of Potential Targets for Therapeutic Intervention
- PMID: 39337309
- PMCID: PMC11432152
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25189821
Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Generation of Absence Seizures: Identification of Potential Targets for Therapeutic Intervention
Abstract
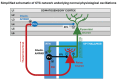
Understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying the generation of absence seizures is crucial for developing effective, patient-specific treatments for childhood absence epilepsy (CAE). Currently, one-third of patients remain refractive to the antiseizure medications (ASMs), previously called antiepileptic drugs (AEDs), available to treat CAE. Additionally, these ASMs often produce serious side effects and can even exacerbate symptoms in some patients. Determining the precise cellular and molecular mechanisms directly responsible for causing this type of epilepsy has proven challenging as they appear to be complex and multifactorial in patients with different genetic backgrounds. Aberrant neuronal activity in CAE may be caused by several mechanisms that are not fully understood. Thus, dissecting the causal factors that could be targeted in the development of precision medicines without side effects remains a high priority and the ultimate goal in this field of epilepsy research. The aim of this review is to highlight our current understanding of potential causative mechanisms for absence seizure generation, based on the latest research using cutting-edge technologies. This information will be important for identifying potential targets for future therapeutic intervention.
Keywords: AMPA receptors; GABA; absence seizures; antiseizure medications; calcium channels; cerebellum; channelopathies; feedforward inhibition; genetic generalized epilepsies; parvalbumin interneurons; personalized medicines; reticular thalamic nucleus; somatosensory cortex; spike-wave discharges; striatum; thalamocortical network; thalamus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Feigin V.L., Nichols E., Alam T., Bannick M.S., Beghi E., Blake N., Culpepper W.J., Dorsey E.R., Elbaz A., Ellenbogen R.G., et al. Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18:459–480. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30499-X. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fisher R.S., Cross J.H., French J.A., Higurashi N., Hirsch E., Jansen F.E., Lagae L., Moshé S.L., Peltola J., Roulet Perez E., et al. Operational classification of seizure types by the International League Against Epilepsy: Position Paper of the ILAE Commission for Classification and Terminology. Epilepsia. 2017;58:522–530. doi: 10.1111/epi.13670. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

