Zeaxanthin and Lutein Ameliorate Alzheimer's Disease-like Pathology: Modulation of Insulin Resistance, Neuroinflammation, and Acetylcholinesterase Activity in an Amyloid-β Rat Model
- PMID: 39337316
- PMCID: PMC11432044
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25189828
Zeaxanthin and Lutein Ameliorate Alzheimer's Disease-like Pathology: Modulation of Insulin Resistance, Neuroinflammation, and Acetylcholinesterase Activity in an Amyloid-β Rat Model
Abstract
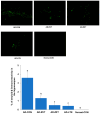
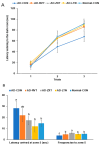
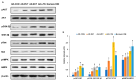
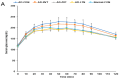
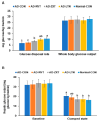
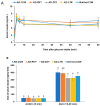
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is characterized by impaired insulin/insulin-like growth factor-1 signaling in the hippocampus. Zeaxanthin and lutein, known for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, have been reported to protect against brain damage and cognitive decline. However, their mechanisms related to insulin signaling in AD remain unclear. This study investigated the efficacy and mechanisms of zeaxanthin, lutein, and resveratrol in modulating an AD-like pathology in an amyloid-β rat model. Rats were administered hippocampal infusions of 3.6 nmol/day amyloid-β (Aβ)(25-35) for 14 days to induce AD-like memory deficits (AD-CON). Normal control rats received Aβ(35-25) (Normal-CON). All rats had a high-fat diet. Daily, AD rats consumed 200 mg/kg body weight of zeaxanthin (AD-ZXT), lutein (AD-LTN), and resveratrol (AD-RVT; positive-control) or resistant dextrin as a placebo (AD-CON) for eight weeks. The AD-CON rats exhibited a higher Aβ deposition, attenuated hippocampal insulin signaling (reduced phosphorylation of protein kinase B [pAkt] and glycogen synthase kinase-3β [pGSK-3β]), increased neuroinflammation, elevated acetylcholinesterase activity, and memory deficits compared to the Normal-CON group. They also showed systemic insulin resistance and high hepatic glucose output. Zeaxanthin and lutein prevented memory impairment more effectively than the positive-control resveratrol by suppressing acetylcholinesterase activity, lipid peroxidation, and pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β). They also potentiated hippocampal insulin signaling and increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and ciliary neurotrophic factor (CTNF) mRNA expression to levels comparable to the Normal-CON rats. Additionally, zeaxanthin and lutein improved glucose disposal, reduced hepatic glucose output, and normalized insulin secretion patterns. In conclusion, zeaxanthin and lutein supplementation at doses equivalent to 1.5-2.0 g daily in humans may have practical implications for preventing or slowing human AD progression by reducing neuroinflammation and maintaining systemic and central glucose homeostasis, showing promise even when compared to the established neuroprotective compound resveratrol. However, further clinical trials are needed to evaluate their efficacy and safety in human populations.
Keywords: carotenoids; hippocampal insulin signaling; memory impairment; systemic insulin resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Tetragonia tetragonioides Protected against Memory Dysfunction by Elevating Hippocampal Amyloid-β Deposition through Potentiating Insulin Signaling and Altering Gut Microbiome Composition.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 21;21(8):2900. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082900. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32326255 Free PMC article.
-
Mitigation of Memory Impairment with Fermented Fucoidan and λ-Carrageenan Supplementation through Modulating the Gut Microbiota and Their Metagenome Function in Hippocampal Amyloid-β Infused Rats.Cells. 2022 Jul 26;11(15):2301. doi: 10.3390/cells11152301. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35892598 Free PMC article.
-
The combination of luteolin and l-theanine improved Alzheimer disease-like symptoms by potentiating hippocampal insulin signaling and decreasing neuroinflammation and norepinephrine degradation in amyloid-β-infused rats.Nutr Res. 2018 Dec;60:116-131. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2018.09.010. Epub 2018 Oct 2. Nutr Res. 2018. PMID: 30527255
-
Medicinal Herbs and Their Derived Ingredients Protect against Cognitive Decline in In Vivo Models of Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 25;23(19):11311. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911311. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-target approach to Alzheimer's disease prevention and treatment: antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and amyloid- modulating mechanisms.Neurogenetics. 2025 Apr 1;26(1):39. doi: 10.1007/s10048-025-00821-y. Neurogenetics. 2025. PMID: 40167826 Review.
Cited by
-
A Systems Biology Approach to Memory Health: Integrating Network Pharmacology, Gut Microbiota, and Multi-Omics for Health Functional Foods.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 12;26(14):6698. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146698. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40724948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotective Mechanisms of Red Algae-Derived Bioactive Compounds in Alzheimer's Disease: An Overview of Novel Insights.Mar Drugs. 2025 Jun 30;23(7):274. doi: 10.3390/md23070274. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40710500 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Park S., Moon N.R., Kang S., Kim D.S. Ferulic acid and vinpocetine intake improves memory function by enhancing insulin sensitivity and reducing neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in type 2 diabetic animals with induced Alzheimer’s disease. J. Funct. Foods. 2022;95:105180. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2022.105180. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

