Development of Novel Alaninamide Derivatives with Anticonvulsant Activity and Favorable Safety Profiles in Animal Models
- PMID: 39337345
- PMCID: PMC11432405
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25189861
Development of Novel Alaninamide Derivatives with Anticonvulsant Activity and Favorable Safety Profiles in Animal Models
Abstract
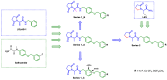
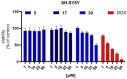
In our current study, we developed a focused series of original ((benzyloxy)benzyl)propanamide derivatives that demonstrated potent activity across in vivo mouse seizure models, specifically, maximal electroshock (MES) and 6 Hz (32 mA) seizures. Among these derivatives, compound 5 emerged as a lead molecule, exhibiting robust protection following intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection, as follows: ED50 = 48.0 mg/kg in the MES test, ED50 = 45.2 mg/kg in the 6 Hz (32 mA) test, and ED50 = 201.3 mg/kg in the 6 Hz (44 mA) model. Additionally, compound 5 displayed low potential for inducing motor impairment in the rotarod test (TD50 > 300 mg/kg), indicating a potentially favorable therapeutic window. In vitro toxicity assays further supported its promising safety profile. We also attempted to identify a plausible mechanism of action of compound 5 by applying both binding and functional in vitro studies. Overall, the data obtained for this lead molecule justifies the more comprehensive preclinical development of compound 5 as a candidate for a potentially broad-spectrum and safe anticonvulsant.
Keywords: amino acids derivatives; anticonvulsant activity; binding/functional assays; hybrid compounds; multimodal/multitarget compounds; tox studies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

