Replicative Endothelial Cell Senescence May Lead to Endothelial Dysfunction by Increasing the BH2/BH4 Ratio Induced by Oxidative Stress, Reducing BH4 Availability, and Decreasing the Expression of eNOS
- PMID: 39337378
- PMCID: PMC11432946
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25189890
Replicative Endothelial Cell Senescence May Lead to Endothelial Dysfunction by Increasing the BH2/BH4 Ratio Induced by Oxidative Stress, Reducing BH4 Availability, and Decreasing the Expression of eNOS
Abstract
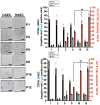
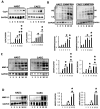
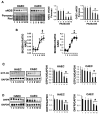
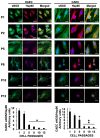
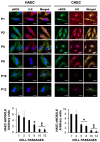
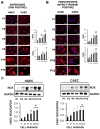
Vascular aging is associated with the development of cardiovascular complications, in which endothelial cell senescence (ES) may play a critical role. Nitric oxide (NO) prevents human ES through inhibition of oxidative stress, and inflammatory signaling by mechanisms yet to be elucidated. Endothelial cells undergo an irreversible growth arrest and alter their functional state after a finite number of divisions, a phenomenon called replicative senescence. We assessed the contribution of NO during replicative senescence of human aortic (HAEC) and coronary (CAEC) endothelial cells, in which accumulation of the senescence marker SA-β-Gal was quantified by β-galactosidase staining on cultured cells. We found a negative correlation in passaged cell cultures from P0 to P12, between a reduction in NO production with increased ES and the formation of reactive oxygen (ROS) and nitrogen (ONOO-) species, indicative of oxidative and nitrosative stress. The effect of ES was evidenced by reduced expression of endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase (eNOS), Interleukin Linked Kinase (ILK), and Heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90), alongside a significant increase in the BH2/BH4 ratio, inducing the uncoupling of eNOS, favoring the production of superoxide and peroxynitrite species, and fostering an inflammatory environment, as confirmed by the levels of Cyclophilin A (CypA) and its receptor Extracellular Matrix Metalloprotease Inducer (EMMPRIN). NO prevents ES by preventing the uncoupling of eNOS, in which oxidation of BH4, which plays a key role in eNOS producing NO, may play a critical role in launching the release of free radical species, triggering an aging-related inflammatory response.
Keywords: Cyclophilin A (CypA); endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) uncoupling; endothelial senescence (ES); extracellular matrix metalloprotease inducer (EMMPRIN); inflammation; nitric oxide (NO); oxidative stress; tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- López-Rivera E., Lizarbe T.R., Martínez-Moreno M., López-Novoa J.M., Rodríguez-Barbero A., Rodrigo J., Fernández A.P., Alvarez-Barrientos A., Lamas S., Zaragoza C. Matrix metalloproteinase 13 mediates nitric oxide activation of endothelial cell migration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2005;102:3685–3690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0408217102. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Herranz B., Marquez S., Guijarro B., Aracil E., Aicart-Ramos C., Rodriguez-Crespo I., Serrano I., Rodríguez-Puyol M., Zaragoza C., Saura M. Integrin-linked kinase regulates vasomotor function by preventing endothelial nitric oxide synthase uncoupling: Role in atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2012;110:439–449. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.253948. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

