New Insights into Mitochondria in Health and Diseases
- PMID: 39337461
- PMCID: PMC11432609
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25189975
New Insights into Mitochondria in Health and Diseases
Abstract
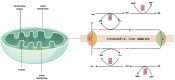
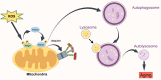
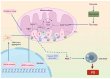
Mitochondria are a unique type of semi-autonomous organelle within the cell that carry out essential functions crucial for the cell's survival and well-being. They are the location where eukaryotic cells carry out energy metabolism. Aside from producing the majority of ATP through oxidative phosphorylation, which provides essential energy for cellular functions, mitochondria also participate in other metabolic processes within the cell, such as the electron transport chain, citric acid cycle, and β-oxidation of fatty acids. Furthermore, mitochondria regulate the production and elimination of ROS, the synthesis of nucleotides and amino acids, the balance of calcium ions, and the process of cell death. Therefore, it is widely accepted that mitochondrial dysfunction is a factor that causes or contributes to the development and advancement of various diseases. These include common systemic diseases, such as aging, diabetes, Parkinson's disease, and cancer, as well as rare metabolic disorders, like Kearns-Sayre syndrome, Leigh disease, and mitochondrial myopathy. This overview outlines the various mechanisms by which mitochondria are involved in numerous illnesses and cellular physiological activities. Additionally, it provides new discoveries regarding the involvement of mitochondria in both disorders and the maintenance of good health.
Keywords: ROS; aging; bioenergetics; mitochondrial; mitochondrial dysfunction; mitochondrial targeted therapy; mtDNA; mutations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

