Comparative Study of the Antioxidant Activity of the Conformers of C-tetra(4-methoxyphenyl)calix[4]resorcinarene
- PMID: 39337498
- PMCID: PMC11432429
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms251810010
Comparative Study of the Antioxidant Activity of the Conformers of C-tetra(4-methoxyphenyl)calix[4]resorcinarene
Abstract
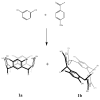
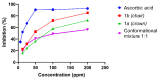
C-tetra(4-methoxyphenyl)calix[4]resorcinarene was synthesized by hydrochloric acid-catalysed cyclocondensation of resorcinol and 4-methoxybenzaldehyde. Under these conditions, the reaction produces a conformational mixture of crown and chair structural conformers, which were separated and characterized by chromatographic and spectroscopic techniques. The antioxidant activity of both conformers was measured by using the DPPH assay, through which it was observed that the chair conformer showed greater antioxidant activity (IC50 = 47.46 ppm) than the crown conformer (IC50 = 78.46 ppm). Additionally, it was observed that the mixture of both conformers presented lower antioxidant activity than either conformer in isolation. The results found suggest that the chair conformer has efficient antioxidant activity that makes it a potential target for further research.
Keywords: antioxidant activity; calix[4]resorcinarene; chair conformer; crown conformer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

