Strongly ROS-Correlated, Time-Dependent, and Selective Antiproliferative Effects of Synthesized Nano Vesicles on BRAF Mutant Melanoma Cells and Their Hyaluronic Acid-Based Hydrogel Formulation
- PMID: 39337557
- PMCID: PMC11432396
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms251810071
Strongly ROS-Correlated, Time-Dependent, and Selective Antiproliferative Effects of Synthesized Nano Vesicles on BRAF Mutant Melanoma Cells and Their Hyaluronic Acid-Based Hydrogel Formulation
Abstract
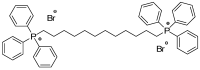
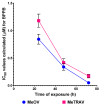
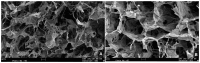
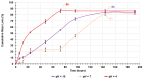
Cutaneous metastatic melanoma (CMM) is the most aggressive form of skin cancer with a poor prognosis. Drug-induced secondary tumorigenesis and the emergency of drug resistance worsen an already worrying scenario, thus rendering urgent the development of new treatments not dealing with mutable cellular processes. Triphenyl phosphonium salts (TPPSs), in addiction to acting as cytoplasmic membrane disruptors, are reported to be mitochondria-targeting compounds, exerting anticancer effects mainly by damaging their membranes and causing depolarization, impairing mitochondria functions and their DNA, triggering oxidative stress (OS), and priming primarily apoptotic cell death. TPP-based bola amphiphiles are capable of self-forming nanoparticles (NPs) with enhanced biological properties, as commonly observed for nanomaterials. Already employed in several other biomedical applications, the per se selective potent antibacterial effects of a TPP bola amphiphile have only recently been demonstrated on 50 multidrug resistant (MDR) clinical superbugs, as well as its exceptional and selective anticancer properties on sensitive and MDR neuroblastoma cells. Here, aiming at finding new molecules possibly developable as new treatments for counteracting CMM, the effects of this TPP-based bola amphiphile (BPPB) have been investigated against two BRAF mutants CMM cell lines (MeOV and MeTRAV) with excellent results (even IC50 = 49 nM on MeOV after 72 h treatment). With these findings and considering the low cytotoxicity of BPPB against different mammalian non-tumoral cell lines and red blood cells (RBCs, selectivity indexes up to 299 on MeOV after 72 h treatment), the possible future development of BPPB as topical treatment for CMM lesions was presumed. With this aim, a biodegradable hyaluronic acid (HA)-based hydrogel formulation (HA-BPPB-HG) was prepared without using any potentially toxic crosslinking agents simply by dispersing suitable amounts of the two ingredients in water and sonicating under gentle heating. HA-BPPB-HA was completely characterized, with promising outcomes such as high swelling capability, high porosity, and viscous elastic rheological behavior.
Keywords: biodegradability; cutaneous metastatic melanoma (CMM); cytotoxicity studies; high porosity; high swelling; hydrogel formulation; low hemolytic effects; mitochondria-targeting molecules; nanosized bola amphiphiles vesicles; triphenyl phosphonium (TPP) groups.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures











References
-
- Hodi F.S., Chiarion -Sileni V., Lewis K.D., Grob J.-J., Rutkowski P., Lao C.D., Cowey C.L., Schadendorf D., Wagstaff J., Dummer R., et al. Long-Term Survival in Advanced Melanoma for Patients Treated with Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab in CheckMate 067. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022;40:9522. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2022.40.16_suppl.9522. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

