RAMP1 Signaling Mitigates Acute Lung Injury by Distinctively Regulating Alveolar and Monocyte-Derived Macrophages
- PMID: 39337592
- PMCID: PMC11432488
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms251810107
RAMP1 Signaling Mitigates Acute Lung Injury by Distinctively Regulating Alveolar and Monocyte-Derived Macrophages
Abstract
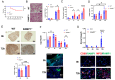
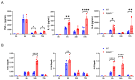
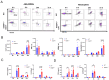
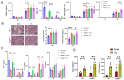
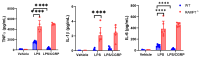
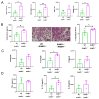
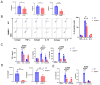
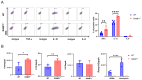
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a life-threatening lung injury that induces cytokine hypersecretion. Receptor activity-modifying protein (RAMP) 1, a subunit of the calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor, regulates the production of cytokines. This study examined the role of RAMP1 signaling during lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute lung injury (ALI). LPS administration to wild-type (WT) mice depleted alveolar macrophages (AMs) and recruited monocyte-derived macrophages (MDMs) and neutrophils. RAMP1-deficient (RAMP1-/-) mice exhibited higher lung injury scores, cytokine levels, and cytokine-producing neutrophil infiltration. RAMP1-deficient AMs produced more cytokines in response to LPS than WT AMs. Adoptive transfer of RAMP1-deficient AMs to RAMP1-/- mice increased cytokine levels and neutrophil accumulation compared to the transfer of WT AMs. RAMP1-/- mice had reduced MDM recruitment and lower pro-inflammatory and reparative macrophage profiles. Cultured bone marrow (BM)-derived RAMP1-deficient macrophages stimulated with LPS showed decreased expression of pro-inflammatory and pro-repairing genes. CGRP administration to WT mice reduced cytokine production and neutrophil accumulation. These findings indicate that RAMP1 signaling mitigates LPS-induced ALI by inactivating AMs and promoting inflammatory and repair activities of MDMs. Targeting RAMP1 signaling presents a potential therapeutic approach for the treatment of ARDS.
Keywords: RAMP1; immunity; macrophage; nerve; neutrophil.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bellani G., Laffey J.G., Pham T., Fan E., Brochard L., Esteban A., Gattinoni L., van Haren F., Larsson A., McAuley D.F., et al. Epidemiology, Patterns of Care, and Mortality for Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Intensive Care Units in 50 Countries. JAMA. 2016;315:788–800. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0291. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Verastegui C., Oliveira A.P., Fernandez-Vivero J., Romero A., de Castro J.M. Calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivity in adult mouse lung. Eur. J. Histochem. 1997;41:119–126. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

