Freeze-Driven Adsorption of Oligonucleotides with polyA-Anchors on Au@Pt Nanozyme
- PMID: 39337597
- PMCID: PMC11432674
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms251810108
Freeze-Driven Adsorption of Oligonucleotides with polyA-Anchors on Au@Pt Nanozyme
Abstract
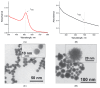
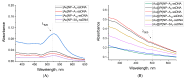
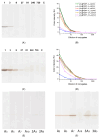
A promising and sought-after class of nanozymes for various applications is Pt-containing nanozymes, primarily Au@Pt, due to their easy preparation and remarkable catalytic properties. This study aimed to explore the freeze-thaw method for functionalizing Pt-containing nanozymes with oligonucleotides featuring a polyadenine anchor. Spherical gold nanoparticles ([Au]NPs) were synthesized and subsequently used as seeds to produce urchin-like Au@Pt nanoparticles ([Au@Pt]NPs) with an average diameter of 29.8 nm. The nanoparticles were conjugated with a series of non-thiolated DNA oligonucleotides, each consisting of three parts: a 5'-polyadenine anchor (An, with n = 3, 5, 7, 10; triple-branched A3, or triple-branched A5), a random sequence of 23 nucleotides, and a linear polyT block consisting of seven deoxythymine residues. The resulting conjugates were characterized using transmission electron microscopy, spectroscopy, dynamic light scattering, and emission detection of the fluorescent label at the 3'-end of each oligonucleotide. The stability of the conjugates was found to depend on the type of oligonucleotide, with decreased stability in the row of [Au@Pt]NP conjugates with A7 > A5 > 3A3 > 3A5 > A10 > A3 anchors. These [Au@Pt]NP-oligonucleotide conjugates were further evaluated using lateral flow test strips to assess fluorescein-specific binding and peroxidase-like catalytic activity. Conjugates with A3, A5, A7, and 3A3 anchors showed the highest levels of signals of bound labels on test strips, exceeding conjugates in sensitivity by up to nine times. These findings hold significant potential for broad application in bioanalytical systems.
Keywords: freeze–thaw method; gold nanoparticles; lateral flow test; nanozymes; oligonucleotide conjugation; peroxidase-like activity; platinum nanoparticles; spherical nucleic acids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Peroxidase-mimicking nanozyme with surface-dispersed Pt atoms for the colorimetric lateral flow immunoassay of C-reactive protein.Mikrochim Acta. 2021 Aug 27;188(9):309. doi: 10.1007/s00604-021-04968-x. Mikrochim Acta. 2021. PMID: 34453188
-
Urchin peroxidase-mimicking Au@Pt nanoparticles as a label in lateral flow immunoassay: impact of nanoparticle composition on detection limit of Clavibacter michiganensis.Mikrochim Acta. 2020 Apr 13;187(5):268. doi: 10.1007/s00604-020-04253-3. Mikrochim Acta. 2020. PMID: 32285207
-
Synthesis of Gold-Platinum Core-Shell Nanoparticles Assembled on a Silica Template and Their Peroxidase Nanozyme Properties.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 8;23(12):6424. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126424. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35742866 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis of rubella virus using antigen-conjugated Au@Pt nanorods as nanozyme probe.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Aug 23;13:4795-4805. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S171429. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30197515 Free PMC article.
-
Biotemplated Platinum Nanozymes: Synthesis, Catalytic Regulation and Biomedical Applications.Chembiochem. 2024 Dec 16;25(24):e202400548. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202400548. Epub 2024 Oct 17. Chembiochem. 2024. PMID: 39166345 Review.
Cited by
-
Sensitive SERS Platform for the Detection of via Freezing SERS Tags and Core-Shell Aptamer-Au@Fe3O4 Nanoparticles.ACS Omega. 2025 Jul 11;10(28):30651-30659. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c02638. eCollection 2025 Jul 22. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40727747 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wu J.J.X., Wang X.Y., Wang Q., Lou Z.P., Li S.R., Zhu Y.Y., Qin L., Wei H. Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): Next-generation artificial enzymes (II) Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019;48:1004–1076. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Q., Song L., Zhang K. Breakthroughs in nanozyme-inspired application diversity. Mater. Chem. Front. 2023;7:44–64. doi: 10.1039/D2QM00960A. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

