Optical Properties and Growth Characteristics of 8-Quinolinolato Lithium (Liq) Nano-Layers Deposited by Gas Transport Deposition
- PMID: 39337749
- PMCID: PMC11434000
- DOI: 10.3390/mi15091089
Optical Properties and Growth Characteristics of 8-Quinolinolato Lithium (Liq) Nano-Layers Deposited by Gas Transport Deposition
Abstract
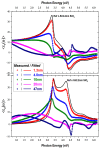
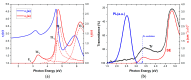
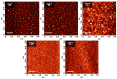
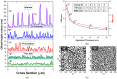
Organometallic complexes containing reactive alkali metals, such as lithium (Li), represent a promising material approach for electron injection layers and electron transport layers (EILs and ETLs) to enhance the performance of Organic Light-Emitting Diodes (OLEDs). 8-Quinolinolato Lithium (Liq) has shown remarkable potential as an EIL and ETL when conveyed in very thin films. Nevertheless, the deposition of nano-layers requires precise control over both thickness and morphology. In this work, we investigate the optical properties and morphological characteristics of Liq thin films deposited via Organic Vapor Phase Deposition (OVPD). Specifically, we present our methodology for analyzing the measured pseudodielectric function <ε(ω)> using Spectroscopic Ellipsometry (SE), alongside the nano-topography of evaporated Liq nano-layers using Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM). This information can contribute to the understanding of the functionality of this material, since ultra-thin Liq interlayers can significantly increase the operational stability of OLED architectures.
Keywords: 8-Quinolinolato Lithium; Liq; OLED; OVPD; Spectroscopic Ellipsometry.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Olaf Wurzinger, Dietmar Keiper, Peter K. Baumann, and Michael Heuken were employed by the company AIXTRON SE. Author Stergios Logothetidis was employed by the company Organic Electronic Technologies (OET). The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Wang S., Zhang H., Zhang B., Xie Z., Wong W.Y. Towards High-Power-Efficiency Solution-Processed OLEDs: Material and Device Perspectives. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2020;140:100547. doi: 10.1016/j.mser.2020.100547. - DOI
-
- Sasabe H., Minamoto K., Pu Y.J., Hirasawa M., Kido J. Ultra High-Efficiency Multi-Photon Emission Blue Phosphorescent OLEDs with External Quantum Efficiency Exceeding 40% Org. Electron. 2012;13:2615–2619. doi: 10.1016/j.orgel.2012.07.019. - DOI
-
- Pode R. Organic Light Emitting Diode Devices: An Energy Efficient Solid State Lighting for Applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020;133:110043. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2020.110043. - DOI
-
- Komatsu R., Sasabe H., Inomata S., Pu Y.J., Kido J. High Efficiency Solution Processed OLEDs Using a Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Emitter. Synth. Met. 2015;202:165–168. doi: 10.1016/j.synthmet.2015.02.009. - DOI
-
- Wu Q., Braveenth R., Bae I.J., Zhang H.Q., Jung H., Kim M., Chai K.Y. Oxadiazole- and Indolocarbazole-Based Bipolar Materials for Green and Yellow Phosphorescent Organic Light Emitting Diodes. Dye Pigment. 2020;174:108052. doi: 10.1016/j.dyepig.2019.108052. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

