Diet and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Scoping Review
- PMID: 39338082
- PMCID: PMC11431716
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph21091199
Diet and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Scoping Review
Abstract
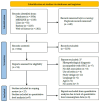
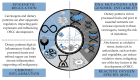
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is the sixth most common type of cancer globally. While smoking is a key risk factor, rising cases in non-smokers highlight the need to explore other factors like diet. This scoping review aims to deepen the evidence on the relationship between OSCC and diet, following PRISMA-ScR guidelines, and was registered on Open Science Framework. Searches were performed in four electronic databases: MEDLINE, Embase, Web of Science, and Lilacs, without date or language restrictions. Studies were evaluated, extracted, and compiled in a narrative table. Seventeen studies with 10,954 patients were analyzed. Most patients were male (74.63%), aged 18-89 (average 50.62). Studies were mainly from high (82%) and medium (17%) Human Development Index (HDI) countries. Dietary surveys included a Food Frequency Questionnaire (FFQ) (58.8%), interviews/questionnaires (17.6%), and an FFQ with a photographic atlas (5.9%). Certain foods in excess like fruits, vegetables, and tea were inversely associated with OSCC, while salty meats, dairy, coffee, sausages, and fried and spicy foods were positively associated. Due to the heterogeneity of the tools used to obtain food frequency data, the results should be interpreted cautiously. New standardized studies and randomized trials are essential to advance understanding and control confounding factors in this field.
Keywords: diet; mouth neoplasms; public health; squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Associations between dietary patterns and head and neck cancer: the Carolina head and neck cancer epidemiology study.Am J Epidemiol. 2012 Jun 15;175(12):1225-33. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwr468. Epub 2012 May 10. Am J Epidemiol. 2012. PMID: 22575416 Free PMC article.
-
Oral human papillomavirus infection, sexual behaviors and risk of oral squamous cell carcinoma in southeast of China: A case-control study.J Clin Virol. 2016 Dec;85:7-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2016.10.011. Epub 2016 Oct 22. J Clin Virol. 2016. PMID: 27788480
-
[Pickled food, fish, seafood intakes and oral squamous cell carcinoma: a case-control study].Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2017 Aug 6;51(8):680-685. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2017.08.005. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28763915 Chinese.
-
Etiologic factors associated with oral squamous cell carcinoma in non-smokers and non-alcoholic drinkers: a brief approach.Braz Dent J. 2012;23(5):586-90. doi: 10.1590/s0103-64402012000500020. Braz Dent J. 2012. PMID: 23306239 Review.
-
Northwestern China: a place to learn more on oesophageal cancer. Part one: behavioural and environmental risk factors.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010 Aug;22(8):917-25. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0b013e3283313d8b. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010. PMID: 20520561 Review.
Cited by
-
Beyond Genetics: Exploring Lifestyle, Microbiome, and Social Determinants in Oral Cancer Development.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Mar 25;17(7):1094. doi: 10.3390/cancers17071094. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40227635 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Cancer Today. [(accessed on 9 April 2024)]. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/en.
-
- Dholam K., Chouksey G. Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Oral Cavity and Oropharynx in Patients Aged 18–45 Years: A Case–Control Study to Evaluate the Risk Factors with Emphasis on Stress, Diet, Oral Hygiene, and Family History. Indian J. Cancer. 2016;53:244–251. - PubMed
-
- Don J., Secchi D.G., Galíndez M.F., Aballay L.R., Pasqualini M.E., Brunotto M. The Association among TP53 Rs1042522, Pri-MiR 34b/c Rs4938723 Polymorphisms and Daily Dietary Fatty Acids in Patients with Premalignant and Malignant Oral Lesions. Hum. Gene. 2022;34:201082. doi: 10.1016/j.humgen.2022.201082. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical