Sustained Long-Term Decline in Anti-HCV Neutralizing Antibodies in HIV/HCV-Coinfected Patients Five Years after HCV Therapy: A Retrospective Study
- PMID: 39338314
- PMCID: PMC11434851
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17091152
Sustained Long-Term Decline in Anti-HCV Neutralizing Antibodies in HIV/HCV-Coinfected Patients Five Years after HCV Therapy: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
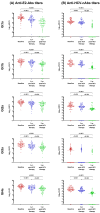
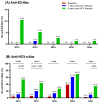
Background: This study evaluated titers and amplitudes of anti-E2 antibodies (anti-E2-Abs) and neutralizing antibodies against hepatitis C virus (HCV; anti-HCV-nAbs) in HIV/HCV-coinfected individuals over five years after successful HCV treatment completion. Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 76 HIV/HCV-coinfected patients achieving sustained virologic response post-HCV treatment. Plasma levels of anti-E2-Abs and anti-HCV-nAbs against five HCV genotypes (Gt1a, Gt1b, Gt2a, Gt3a, and Gt4a) were determined using ELISA and microneutralization assays, respectively. Statistical analyses comparing the three follow-up time points (baseline, one year, and five years post-HCV treatment) were performed using generalized linear mixed models, adjusting p-values with the false discovery rate (q-value). Results: Compared to baseline, anti-E2-Abs titers decreased at one year (1.9- to 2.3-fold, q-value < 0.001) and five years (3.4- to 9.1-fold, q-value < 0.001) post-HCV treatment. Anti-HCV-nAbs decreased 2.9- to 8.4-fold (q-value < 0.002) at one year and 17.8- to 90.4-fold (q-value < 0.001) at five years post-HCV treatment. Anti-HCV-nAbs titers against Gt3a were consistently the lowest. Nonresponse rates for anti-E2-Abs remained low throughout the follow-up, while anti-HCV-nAbs nonresponse rates increased 1.8- to 13.5-fold (q-value < 0.05) at five years post-HCV treatment, with Gt3a showing the highest nonresponse rate. Conclusions: Humoral immune responses against HCV decreased consistently one and five years post-HCV treatment, regardless of HCV genotype and previous HCV therapy or type of treatment (IFN- or DAA-based therapy). This decline was more pronounced for anti-HCV-nAbs, particularly against Gt3.
Keywords: HIV; HIV/HCV coinfection; anti-HCV therapy; broad-spectrum neutralizing antibodies; hepatitis C; sustained virologic response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Negative impact of HIV infection on broad-spectrum anti-HCV neutralizing antibody titers in HCV-infected patients with advanced HCV-related cirrhosis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Jun;150:113024. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113024. Epub 2022 Apr 25. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 35483197
-
Persistent Low Anti-HIV Neutralizing Antibody Titers in HIV/HCV Coinfection Despite HCV Cure: A 5-Year Longitudinal Analysis.Vaccines (Basel). 2025 May 19;13(5):539. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13050539. Vaccines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40432148 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid decrease in titer and breadth of neutralizing anti-HCV antibodies in HIV/HCV-coinfected patients who achieved SVR.Sci Rep. 2019 Aug 21;9(1):12163. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48592-5. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31434968 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of chronic HCV genotype 1 coinfection.Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2015 Sep;12(3):326-35. doi: 10.1007/s11904-015-0278-4. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2015. PMID: 26228050 Review.
-
Treatment of hepatitis C in HIV-coinfected patients.Ann Pharmacother. 2006 Mar;40(3):479-89; quiz 582-3. doi: 10.1345/aph.1G427. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Ann Pharmacother. 2006. PMID: 16507622 Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Dengue—Global Situation. 2024. [(accessed on 10 July 2024)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/disease-outbreak-news/item/2024-DON518.
-
- World Health Organization Guidelines for the Care and Treatment of Persons Diagnosed with Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection. [(accessed on 21 August 2024)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241550345. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- PI20/00474/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- PI17/00657/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- PI20/00507/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- PI17/00903/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- PI19CIII/00009/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- PI23CIII/00018/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- PI20CIII/00004/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- PI17CIII/00003/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- CP23CIII/00004/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- CB21/13/00044/CIBER -Consorcio Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red- (CB 2021), Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación and Unión Europea - NextGenerationEU
- CB21/13/00039/CIBER -Consorcio Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red- (CB 2021), Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación and Unión Europea - NextGenerationEU
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

