Synthesis of New Thiazole-Privileged Chalcones as Tubulin Polymerization Inhibitors with Potential Anticancer Activities
- PMID: 39338317
- PMCID: PMC11435058
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17091154
Synthesis of New Thiazole-Privileged Chalcones as Tubulin Polymerization Inhibitors with Potential Anticancer Activities
Abstract
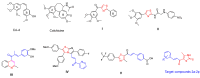
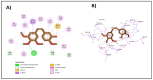
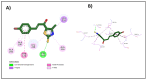
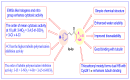
A series of novel thiazole-based chalcones were evaluated for their anticancer activity as potential tubulin polymerization inhibitors. In vitro anticancer screening for the thiazole derivatives 2a-2p exhibited broad-spectrum antitumor activity against various cancer cell lines particularly Ovar-3 and MDA-MB-468 cells with a GI50 range from 1.55 to 2.95 μΜ, respectively. Compound 2e demonstrated significant inhibition of tubulin polymerization, with an IC50 value of 7.78 μM compared to Combretastatin-A4 (CA-4), with an IC50 value of 4.93 μM. Molecular docking studies of compounds 2e, 2g, and 2h into tubulin further supported these findings, revealing that they bind effectively to the colchicine binding site, mirroring key interactions exhibited by CA-4. Computational predictions suggested favorable oral bioavailability and drug-likeness for these compounds, highlighting their potential for further development as chemotherapeutic agents.
Keywords: anticancer; colchicine binding site; thiazole chalcones; tubulin inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that this study received No funding from Apogee Pharmaceuticals Inc. The funder was not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, the writing of this article or the decision to submit it for publication.
Figures








References
-
- Mohammed H.H.H., El-Hafeez A.A.A., Ebeid K., Mekkawy A.I., Abourehab M.A.S., Wafa E.I., Alhaj-Suliman S.O., Salem A.K., Ghosh P., Abuo-Rahma G.E.-D.A., et al. New 1,2,3-triazole linked ciprofloxacin-chalcones induce DNA damage by inhibiting human topoisomerase I&II and tu-bulin polymerization. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2022;37:1346–1363. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2022.2072308. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mohammed H.H.H., El-Hafeez A.A.A., Abbas S.H., Abdelhafez E.-S.M.N., Abuo-Rahma G.E.-D.A. New antiproliferative 7-(4-(N-substituted carbamoylmethyl)piperazin-1-yl) derivatives of ciprofloxacin induce cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016;24:4636–4646. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2016.07.070. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yan J., Xu Y., Jin X., Zhang Q., Ouyang F., Han L., Zhan M., Li X., Liang B., Huang X. Structure modification and biological evaluation of indole-chalcone derivatives as anti-tumor agents through dual targeting tubulin and TrxR. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022;227:113897. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113897. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

