Anxiolytic and Antidepressant Effects of Tribulus terrestris Ethanolic Extract in Scopolamine-Induced Amnesia in Zebrafish: Supported by Molecular Docking Investigation Targeting Monoamine Oxidase A
- PMID: 39338370
- PMCID: PMC11434784
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17091208
Anxiolytic and Antidepressant Effects of Tribulus terrestris Ethanolic Extract in Scopolamine-Induced Amnesia in Zebrafish: Supported by Molecular Docking Investigation Targeting Monoamine Oxidase A
Abstract
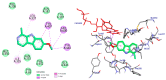
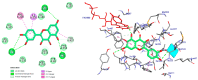
Plants of the genus Tribulus have been used in folk medicine for wound healing, alleviating liver, stomach, and rheumatism pains, and as cognitive enhancers, sedatives, antiseptics, tonics, and stimulants. The present work aimed to evaluate whether Tribulus terrestris (Tt) administered for 15 days attenuated cognitive deficits and exhibited anxiolytic and antidepressant profiles in scopolamine-induced amnesia in zebrafish. Animals were randomly divided into six groups (eight animals per group): (1)-(3) Tt treatment groups (1, 3 and 6 mg/L), (4) control, (5) scopolamine (SCOP, 0.7 mg/kg), and (6) galantamine (Gal, 1 mg/L). Exposure to SCOP (100 µM) resulted in anxiety in zebrafish, as assessed by the novel tank diving test (NTT) and novel approach test (NAT). When zebrafish were given SCOP and simultaneously given Tt (1, 3, and 6 mg/L once daily for 10 days), the deficits were averted. Molecular interactions of chemical compounds from the Tt fractions with the monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) were investigated via molecular docking experiments. Using behavioral experiments, we showed that administration of Tt induces significant anxiolytic-antidepressant-like effects in SCOP-treated zebrafish. Our result indicated that flavonoids of Tt, namely kaempferol, quercetin, luteolin, apigetrin, and epigallocatechin, could act as promising phytopharmaceuticals for improving anxiety-related disorders.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; NTT; depression; kaempferol; locomotor activity; monoamine oxidase A.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

