Effect of Opaganib on Supplemental Oxygen and Mortality in Patients with Severe SARS-CoV-2 Based upon FIO2 Requirements
- PMID: 39338442
- PMCID: PMC11434591
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms12091767
Effect of Opaganib on Supplemental Oxygen and Mortality in Patients with Severe SARS-CoV-2 Based upon FIO2 Requirements
Abstract
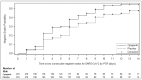
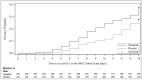
Once a patient has been diagnosed with severe COVID-19 pneumonia, treatment options have limited effectiveness. Opaganib is an oral treatment under investigation being evaluated for treatment of hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia. A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind phase 2/3 trial was conducted in 57 sites worldwide from August 2020 to July 2021. Patients received either opaganib (n = 230; 500 mg twice daily) or matching placebo (n = 233) for 14 days. The primary outcome was the proportion of patients no longer requiring supplemental oxygen by day 14. Secondary outcomes included changes in the World Health Organization Ordinal Scale for Clinical Improvement, viral clearance, intubation, and mortality at 28 and 42 days. Pre-specified primary and secondary outcome analyses did not demonstrate statistically significant benefit (except nominally for time to viral clearance). Post-hoc analysis revealed the fraction of inspired oxygen (FIO2) at baseline was prognostic for opaganib treatment responsiveness and corresponded to disease severity markers. Patients with FIO2 levels at or below the median value (≤60%) had better outcomes after opaganib treatment (n = 117) compared to placebo (n = 134). The proportion of patients with ≤60% FIO2 at baseline that no longer required supplemental oxygen (≥24 h) by day 14 of opaganib treatment increased (76.9% vs. 63.4%; nominal p-value = 0.033). There was a 62.6% reduction in intubation/mechanical ventilation (6.84% vs. 17.91%; nominal p-value = 0.012) and a clinically meaningful 62% reduction in mortality (5.98% vs. 16.7%; nominal p-value = 0.019) by day 42. No new safety concerns were observed. While the primary analyses were not statistically significant, post-hoc analysis suggests opaganib benefit for patients with severe COVID-19 requiring supplemental oxygen with an FIO2 of ≤60%. Further studies are warranted to prospectively confirm opaganib benefit in this subpopulation.
Keywords: ABC294640; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia; opaganib; sphingosine kinase 2; trial registration number: NCT04467840.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Ofra Barnett-Griness, Rachael lask Gerlach, Eppie Campbell, Aida Bibliowicz, Reza Fathi, Patricia Anderson, Gilead Raday, Vered Katz Ben-Yair, Mark L. Levitt, Clara Fehrmann and Gina Eagle were employed by the companies Bioforum Ltd., RedHill Biopharma Ltd, CEEF Solutions Beaconsfield and G.E.T. Pharma Consulting, LLC. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- WHO COVID-19 Dashboard. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2020. [(accessed on 15 June 2023)]. Updated Daily. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/
-
- World Health Organization Classification of Omicron (B.1.1.529): SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern. Published 26 November 2021. [(accessed on 20 July 2022)]; Available online: www.who.int/news/item/26-11-2021-classification-of-omicron-(b.1.1.529)-s....
-
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration Coronavirus (COVID-19): Drugs. Date Last Updated: 29 December 2023. [(accessed on 5 May 2024)]; Available online: www.fda.gov/drugs/emergency-preparedness-drugs/coronavirus-covid-19-drugs.
-
- French K.J., Zhuang Y., Maines L.W., Gao P., Wang W., Beljanski V., Upson J.J., Green C.L., Keller S.N., Smith C.D. Pharmacology and antitumor activity of ABC294640, a selective inhibitor of sphingosine kinase-2. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010;333:129–139. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.163444. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

