Physicochemical, Sensory, and Microbiological Analysis of Fermented Drinks Made from White Kidney Bean Extract and Cow's Milk Blends during Refrigerated Storage
- PMID: 39338506
- PMCID: PMC11433744
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms12091832
Physicochemical, Sensory, and Microbiological Analysis of Fermented Drinks Made from White Kidney Bean Extract and Cow's Milk Blends during Refrigerated Storage
Abstract
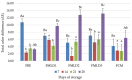
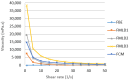
Due to its low dietary impact and bioactive compounds, such as polyphenols and flavonoids, white kidney bean extract is an attractive raw material for fermented drinks. It can be utilized either on its own or blended with cow's milk, offering a promising solution to help meet dairy product demand during mid-season shortages. Therefore, this study aimed to explore the physicochemical characteristics, sensory properties, and microbiological profile of fermented milk-like drinks made from white kidney bean extract, cow's milk and their blends during 28 days of storage at 4 °C. Three blends of fermented milk-like drinks (FMLDs) were prepared from different ratios of cow's milk (CM) and kidney bean extract (BE): FMLD1 (CM 30%:BE 70%); FMLD2 (CM 50%:BE 50%), FMLD3 (CM 70%:BE 30%), along with plain fermented kidney been extract (FBE; CM 0%:BE 100%), and plain fermented cow's milk (FCM; CM 100%:BE 0%). The mixtures were pasteurized at 92 °C for 25 min and fermented with a probiotic-type starter culture (S. thermophilus, B. bifidum, L. acidophilus) at 43 °C. FBE exhibited the lowest levels of carbohydrates (2.14%), fat (0.11%), and protein (1.45%) compared to fermented cow's milk and blends. The FBE and the fermented blends with a higher ratio of bean extract had lower viscosity and lactic acid contents, greener hue, more pronounced aftertaste and off-flavors, and received lower overall acceptability scores. Although the FCM had higher counts of S. thermophilus and L. acidophilus, the FBE displayed significantly higher counts of B. bifidum. This study demonstrated the potential of using white kidney bean extract and its blends with cow's milk to create unique fermented products with a lower dietary impact, highlighting the importance of further optimizing the formulations to enhance sensory qualities and reduce the beany off-flavors in the products with added kidney bean extract.
Keywords: blends; cow’s milk; fermentation; probiotic-type strains; white kidney bean extract.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Development of fermented milk product based on mare milk and lactic microorganisms association].Vopr Pitan. 2021;90(5):115-125. doi: 10.33029/0042-8833-2021-90-5-115-125. Epub 2021 Sep 1. Vopr Pitan. 2021. PMID: 34719149 Russian.
-
Physical, Chemical, Microbiological and Sensory Characteristics of a Probiotic Beverage Produced from Different Mixtures of Cow's Milk and Soy Beverage by Lactobacillus acidophilus La5 and Yoghurt Culture.Food Technol Biotechnol. 2019 Dec;57(4):461-471. doi: 10.17113/ftb.57.04.19.6344. Food Technol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 32123508 Free PMC article.
-
Color Stability of Fermented Mare's Milk and a Fermented Beverage from Cow's Milk Adapted to Mare's Milk Composition.Foods. 2020 Feb 19;9(2):217. doi: 10.3390/foods9020217. Foods. 2020. PMID: 32092908 Free PMC article.
-
Cow's Milk Processing-Friend or Foe in Food Allergy?Foods. 2021 Mar 9;10(3):572. doi: 10.3390/foods10030572. Foods. 2021. PMID: 33803451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Foods for Special Dietary Needs: Non-dairy Plant-based Milk Substitutes and Fermented Dairy-type Products.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2016;56(3):339-49. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2012.761950. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2016. PMID: 25575046 Review.
References
-
- Los F., Zielinski A., Wojeicchowski J., Nogueira A., Demiate I. Beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.): Whole Seeds with Complex Chemical Composition. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2018;19:63–71. doi: 10.1016/j.cofs.2018.01.010. - DOI
-
- Makulbekova A., Iskakov A., Kulkarni K.P., Song J.T., Lee J.-D. Current Status and Future Prospects of Soybean Production in Kazakhstan. Plant Breed. Biotechnol. 2017;5:55–66. doi: 10.9787/PBB.2017.5.2.55. - DOI
-
- Manasa R., Harshita, Prakruthi M., Shekahara Naik R., Mahesh S. Non-Dairy Plant Based Beverages: A Comprehensive Review. Pharma Innov. J. 2020;9:258–271.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

