Binary and Ternary Inclusion Complexes of Niflumic Acid: Synthesis, Characterization, and Dissolution Profile
- PMID: 39339226
- PMCID: PMC11435181
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16091190
Binary and Ternary Inclusion Complexes of Niflumic Acid: Synthesis, Characterization, and Dissolution Profile
Abstract
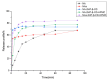
Although niflumic acid (NA) is one of the most used non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, it suffers from poor solubility, low bioavailability, and significant adverse effects. To address these limitations, the complexation of NA with cyclodextrins (CDs) is a promising strategy. However, complexing CDs with low molecular weight drugs like NA can lead to low CE. This study explores the development of inclusion complexes of NA with 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (2HP-β-CD), including the effect of converting NA to its sodium salt (NAs) and adding hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) on complex formation. Inclusion complexes were prepared using co-evaporation solvent and freeze-drying methods, and their CE and Ks were determined through a phase solubility study. The complexes were characterized using physicochemical analyses, including FT-IR, DSC, SEM, XRD, DLS, UV-Vis, 1H-NMR, and 1H-ROESY. The dissolution profiles of the complexes were also evaluated. The analyses confirmed complex formation for all systems, demonstrating drug-cyclodextrin interactions, amorphous drug states, morphological changes, and improved solubility and dissolution profiles. The NAs-2HP-β-CD-HPMC complex exhibited the highest CE and Ks values, a 1:1 host-guest molar ratio, and the best dissolution profile. The results indicate that the NAs-2HP-β-CD-HPMC complex has potential for delivering NA, which might enhance its therapeutic effectiveness and minimize side effects.
Keywords: 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin; complexation efficiency; dissolution profile; drug delivery; inclusion complex; niflumic acid; solubility.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures











References
-
- Pandey S.P., Shukla T., Dhote V.K., Mishra D.K., Maheshwari R., Tekade R.K. Use of polymers in controlled release of active agents. In: Tekade R.K., editor. Advances in Pharmaceutical Product Development and Research, Basic Fundamentals of Drug Delivery. Academic Press; New York, NY, USA: 2019. pp. 113–172.
-
- Szunyogh T., Ambrus R., Szabó-Révész P. Nanonization of niflumic acid by co-grinding. Adv. Nanoparticles. 2013;2:329–335. doi: 10.4236/anp.2013.24045. - DOI
-
- Bag P.P., Reddy C.M. Screening and selective preparation of polymorphs by fast evaporation method: A case study of aspirin, anthranilic acid, and niflumic acid. Cryst. Growth Des. 2012;12:2740–2743. doi: 10.1021/cg300404r. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

