Oral Gels as an Alternative to Liquid Pediatric Suspensions Compounded from Commercial Tablets
- PMID: 39339265
- PMCID: PMC11434729
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16091229
Oral Gels as an Alternative to Liquid Pediatric Suspensions Compounded from Commercial Tablets
Abstract
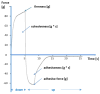
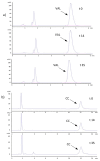
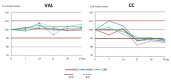
The aim of the study was to propose pharmacy-compounded oral gels as a new and alternative dosage form that is attractive to children as having a better masking taste than syrups and reducing the risk of spilling. The application and physical properties of the gels prepared with cellulose derivatives (hydroxyethylcellulose and carmellose sodium) or carbomers were evaluated. The results of the study showed the most suitable consistency, viscosity, and organoleptic properties for gels prepared with carbomer and cellulose derivatives at concentrations of 0.75% and 2.0%, respectively. The microbial stability of the gels was guaranteed by the use of methylparaben and potassium sorbate. VAL (valsartan) and CC (candesartan cilexetil) tablets, often used off-label in children, were pulverized and suspended in the hydrogel bases, resulting in final drug concentrations of 4 mg/g and 1 mg/g, respectively. There was no significant change in viscosity and consistency parameters when the pulverized tablets were added, and only small changes in viscosity and consistency were observed during 35 days of storage, especially in the gels with sodium carmellose and candesartan. On the basis of the drug assay, an expiry date of 25 °C was recommended: 35 days for valsartan and 14 days for candesartan preparations.
Keywords: candesartan cilexetil; carbomer; cellulose polymers; pediatric oral gels; stability; valsartan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- WHO Development of Paediatric Medicines: Points to Consider in Formulation. [(accessed on 12 September 2024)];WHO Tech. Rep. Series. 2012 970:197–225. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/trs970-annex-5-development-of-pa....
-
- Alessandrini E., Brako F., Scarpa M., Lupo M., Bonifazi D., Pignataro V., Cavallo M., Cullufe O., Enache C., Nafria B., et al. Children’s preferences for oral dosage forms and their involvement in formulation research via EPTRI (European Paediatric Translational Research Infrastructure) Pharmaceutics. 2021;13:730. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13050730. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

