Privileged Scaffold Hybridization in the Design of Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
- PMID: 39339439
- PMCID: PMC11433937
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29184444
Privileged Scaffold Hybridization in the Design of Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
Abstract
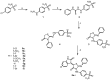
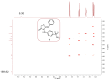
Human Carbonic Anhydrases (hCA) are enzymes that contribute to cancer's development and progression. Isoforms IX and XII have been identified as potential anticancer targets, and, more specifically, hCA IX is overexpressed in hypoxic tumor cells, where it plays an important role in reprogramming the metabolism. With the aim to find new inhibitors towards IX and XII isoforms, the hybridization of the privileged scaffolds isatin, dihydrothiazole, and benzenesulfonamide was investigated in order to explore how it may affect the activity and selectivity of the hCA isoforms. In this respect, a series of isatin thiazolidinone hybrids have been designed and synthesized and their biological activity and selectivity on hCA I, hCA II, hCA IX, and hCA XII explored. The new compounds exhibited promising inhibitory activity results on isoforms IX and XII in the nanomolar range, which has highlighted the importance of substituents in the isatin ring and in position 3 and 5 of thiazolidinone. In particular, compound 5g was the most active toward hCA IX, while 5f was the most potent inhibitor of hCA XII within the series. When both potency and selectivity were considered, compound 5f appeared as one of the most promising. Additionally, our investigations were supported by molecular docking experiments, which have highlighted the putative binding poses of the most promising compound.
Keywords: benzenesulfonamide-based zinc binders; carbonic anhydrases inhibitors; scaffold hybridization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Salamat M.S. Robbins and Cotran: Pathologic Basis of Disease, 8th Edition. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2010;69:214. doi: 10.1097/NEN.0b013e3181cd8dbc. - DOI
-
- Fabianova A., Barathova M., Csaderova L., Simko V., Zatovicova M., Labudova M., Pastorek J. Hypoxic marker CA IX and adhesion mediator beta-catenin are downregulated by lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus persistent infection. Oncotarget. 2018;9:12879–12893. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.24387. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

