Akkermansia muciniphila as a Potential Guardian against Oral Health Diseases: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 39339675
- PMCID: PMC11434887
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16183075
Akkermansia muciniphila as a Potential Guardian against Oral Health Diseases: A Narrative Review
Abstract
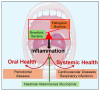
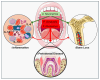
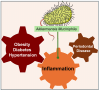
The oral microbiome is a diverse ecosystem containing a community of symbiotic, commensal, and pathogenic microorganisms. One key microorganism linked to periodontal disease (PD) is Porphyromonas gingivalis (P. gingivalis), a Gram-negative anaerobic bacterium known to have several virulence factors that trigger inflammation and immune evasion. On the other hand, Akkermansia muciniphila (A. muciniphila), a symbiotic bacterium, has been recently shown to play an important role in mitigating inflammation and reducing periodontal damage. In vivo and in vitro studies have shown that A. muciniphila decreases inflammatory mediators and improves immune responses, suggesting its role in mitigating PD and related inflammatory systemic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and obesity. This review discusses the anti-inflammatory effects of A. muciniphila, its impact on periodontal health, and its potential role in managing systemic diseases. The overall aim is to elucidate how this bacterium might help reduce inflammation, improve oral health, and influence broader health outcomes.
Keywords: Akkermansia muciniphila; diabetes; diet; dysbiosis; hypertension; inflammation; obesity; oral health; periodontal disease; prebiotics; probiotics; short chain fatty acids; systemic diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Lu M., Xuan S., Wang Z. Oral microbiota: A new view of body health. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness. 2019;8:8–15. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2018.12.001. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

