Daidzein Inhibits Muscle Atrophy by Suppressing Inflammatory Cytokine- and Muscle Atrophy-Related Gene Expression
- PMID: 39339684
- PMCID: PMC11434955
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16183084
Daidzein Inhibits Muscle Atrophy by Suppressing Inflammatory Cytokine- and Muscle Atrophy-Related Gene Expression
Abstract
Background: Sarcopenic obesity, which is associated with a poorer prognosis than that of sarcopenia alone, may be positively affected by soy isoflavones, known inhibitors of muscle atrophy. Herein, we hypothesize that these compounds may prevent sarcopenic obesity by upregulating the gut metabolites with anti-inflammatory effects.
Methods: To explore the effects of soy isoflavones on sarcopenic obesity and its mechanisms, we employed both in vivo and in vitro experiments. Mice were fed a high-fat, high-sucrose diet with or without soy isoflavone supplementation. Additionally, the mouse C2C12 myotube cells were treated with palmitic acid and daidzein in vitro.
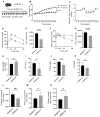
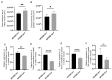
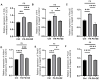
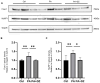
Results: The isoflavone considerably reduced muscle atrophy and the expression of the muscle atrophy genes in the treated group compared to the control group (Fbxo32, p = 0.0012; Trim63, p < 0.0001; Foxo1, p < 0.0001; Tnfa, p = 0.1343). Elevated levels of daidzein were found in the muscles and feces of the experimental group compared to the control group (feces, p = 0.0122; muscle, p = 0.0020). The real-time PCR results demonstrated that the daidzein decreased the expression of the palmitate-induced inflammation and muscle atrophy genes in the C2C12 myotube cells (Tnfa, p = 0.0201; Il6, p = 0.0008; Fbxo32, p < 0.0001; Hdac4, p = 0.0002; Trim63, p = 0.0114; Foxo1, p < 0.0001). Additionally, it reduced the palmitate-induced protein expression related to the muscle atrophy in the C2C12 myotube cells (Foxo1, p = 0.0078; MuRF1, p = 0.0119).
Conclusions: The daidzein suppressed inflammatory cytokine- and muscle atrophy-related gene expression in the C2C12 myotubes, thereby inhibiting muscle atrophy.
Keywords: C2C12 myotubes; daidzein; high-fat diet; high-sucrose diet; mice; muscle atrophy; sarcopenia; sarcopenic obesity; soy isoflavones.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Nakajima H received personal fees from Kowa Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co., Ltd., and Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ltd. Dr. Ushigome received grant support from the Japanese Study Group for Physiology and Management of Blood Pressure, the Astellas Foundation for Research on Metabolic Disorders (Grant number: 4024) Mishima Kaiun Memorial Foundation, and received personal fees from Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ltd., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., MSD K.K., Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co., Ltd., Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma Co., Ltd., Kowa Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Novo Nordisk Pharma Ltd., Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Taisho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Sanofi K.K., outside the submitted work. Donated Fund Laboratory of Diabetes therapeutics is an endowment department, supported with an unrestricted grant from Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Taiyo Kagaku Co., Ltd. and Taisho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Dr. Okada received personal fees from Mochida Pharma Co., Ltd., Teijin Pharma Ltd., MSD K.K., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, AstraZeneca K.K., Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma Co., Ltd., Novo Nordisk Pharma Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K, Kyowa Hakko Kirin Company Ltd., Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Kowa Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Sanofi K.K. Dr, Nakanishi received personal fees from Kowa Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Novo Nordisk Pharma Ltd., Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ltd., TERUMO CORPORATION. Dr. Hamaguchi received grants from AstraZeneca K.K., Ono Pharma Co., Ltd., Kowa Pharma Co., Ltd.; and received personal fees from AstraZeneca K.K., Ono Pharma Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly, Japan, Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma Co., Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corp., Sanofi K.K., K.K., and Kowa Pharma Co., Ltd. outside of the submitted work. Prof. Fukui received grants from Ono Pharma Co., Ltd., Oishi Kenko inc., Yamada Bee Farm, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ltd., Kissei Pharma Co., Ltd., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corp., Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., Sanofi K.K., Takeda Pharma Co., Ltd., Astellas Pharma Inc., MSD K.K., Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd., Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma Co., Ltd., Kowa Pharma Co., Ltd., Novo Nordisk Pharma Ltd., Sanwa Kagagu Kenkyusho CO., Ltd., Eli Lilly, Japan, K.K., Taisho Pharma Co., Ltd., Terumo Corp., Tejin Pharma Ltd., Nippon Chemiphar Co., Ltd., Abbott Japan Co., Ltd., and Johnson & Johnson K.K. Medical Co., TERUMO CORPORATION, and received personal fees from Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ltd., Kissei Pharma Co., Ltd., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corp., Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., Sanofi K.K., Takeda Pharma Co., Ltd., Astellas Pharma Inc., MSD K.K., Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd., Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma Co., Ltd., Kowa Pharma Co., Ltd., Novo Nordisk Pharma Ltd., Ono Pharma Co., Ltd., Sanwa Kagaku Kenkyusho Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Taisho Pharma Co., Ltd., Bayer Yakuhin, Ltd., AstraZeneca K.K., Mochida Pharma Co., Ltd., Abbott Japan Co., Ltd., Teijin Pharma Ltd., Arkray Inc., Medtronic Japan Co., Ltd., and Nipro Corp., TERUMO CORPORATION, outside the submitted work. The other authors have no competing interests to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Cruz-Jentoft A.J., Baeyens J.P., Bauer J.M., Boirie Y., Cederholm T., Landi F., Martin F.C., Michel J.P., Rolland Y., Schneider S.M., et al. Sarcopenia: European Consensus on Definition and Diagnosis: Report of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Age Ageing. 2010;39:412–423. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afq034. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Celis-Morales C.A., Welsh P., Lyall D.M., Steell L., Petermann F., Anderson J., Iliodromiti S., Sillars A., Graham N., MacKay D.F., et al. Associations of Grip Strength with Cardiovascular, Respiratory, and Cancer Outcomes and All Cause Mortality: Prospective Cohort Study of Half a Million UK Biobank Participants. BMJ. 2018;361:k1651. doi: 10.1136/bmj.k1651. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

