The Impact of Yoyo Dieting and Resistant Starch on Weight Loss and Gut Microbiome in C57Bl/6 Mice
- PMID: 39339738
- PMCID: PMC11435396
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16183138
The Impact of Yoyo Dieting and Resistant Starch on Weight Loss and Gut Microbiome in C57Bl/6 Mice
Abstract
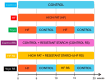
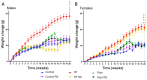
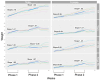
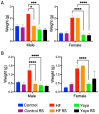
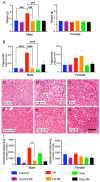
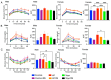
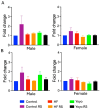
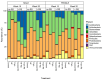
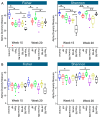
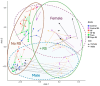
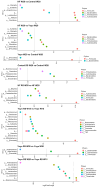
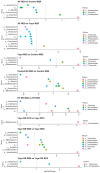
Cyclic weight loss and subsequent regain after dieting and non-dieting periods, a phenomenon termed yoyo dieting, places individuals at greater risk of metabolic complications and alters gut microbiome composition. Resistant starch (RS) improves gut health and systemic metabolism. This study aimed to investigate the effect of yoyo dieting and RS on the metabolism and gut microbiome. C57BL/6 mice were assigned to 6 diets for 20 weeks, including control, high fat (HF), yoyo (alternating HF and control diets every 5 weeks), control with RS, HF with RS, and yoyo with RS. Metabolic outcomes and microbiota profiling using 16S rRNA sequencing were examined. Yoyo dieting resulted in short-term weight loss, which led to improved liver health and insulin tolerance but also a greater rate of weight gain compared to continuous HF feeding, as well as a different microbiota profile that was in an intermediate configuration between the control and HF states. Mice fed HF and yoyo diets supplemented with RS gained less weight than those fed without RS. RS supplementation in yoyo mice appeared to shift the gut microbiota composition closer to the control state. In conclusion, yoyo dieting leads to obesity relapse, and increased RS intake reduces weight gain and might help prevent rapid weight regain via gut microbiome restoration.
Keywords: fatty liver; gut microbiome; metabolism; obesity; resistant starch; short-chain fatty acid; weight cycling; yoyo dieting.
Conflict of interest statement
M.O’H. has a financial interest in Prevatex Pty Ltd., a company developing probiotic-based biotherapeutics. Other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

