The Autophagy Receptor SQSTM1/p62 Is a Restriction Factor of HCMV Infection
- PMID: 39339916
- PMCID: PMC11436200
- DOI: 10.3390/v16091440
The Autophagy Receptor SQSTM1/p62 Is a Restriction Factor of HCMV Infection
Abstract
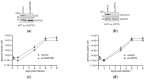
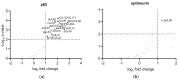
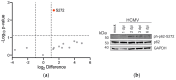
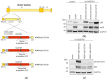
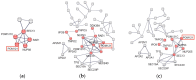
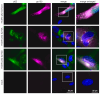
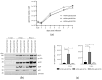
(1) Background: Intrinsic defense mechanisms are pivotal host strategies to restrict viruses already at early stages of their infection. Here, we addressed the question of how the autophagy receptor sequestome 1 (SQSTM1/p62, hereafter referred to as p62) interferes with human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection. (2) Methods: CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing, mass spectrometry and the expression of p62 phosphovariants from recombinant HCMVs were used to address the role of p62 during infection. (3) Results: The knockout of p62 resulted in an increased release of HCMV progeny. Mass spectrometry revealed an interaction of p62 with cellular proteins required for nucleocytoplasmic transport. Phosphoproteomics further revealed that p62 is hyperphosphorylated at position S272 in HCMV-infected cells. Phosphorylated p62 showed enhanced nuclear retention, which is concordant with enhanced interaction with viral proteins relevant for genome replication and nuclear capsid egress. This modification led to reduced HCMV progeny release compared to a non-phosphorylated version of p62. (4) Conclusions: p62 is a restriction factor for HCMV replication. The activity of the receptor appears to be regulated by phosphorylation at position S272, leading to enhanced nuclear localization, viral protein degradation and impaired progeny production.
Keywords: SQSTM1/p62; autophagy receptor; host cell defense; human cytomegalovirus; optineurin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

