Evaluation of Vaccine Strategies among Healthcare Workers during COVID-19 Omicron Outbreak in Taiwan
- PMID: 39340088
- PMCID: PMC11435596
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines12091057
Evaluation of Vaccine Strategies among Healthcare Workers during COVID-19 Omicron Outbreak in Taiwan
Abstract
Background/objectives: This study aimed to assess the reactogenicity and immunogenicity of various SARS-CoV-2 vaccines and compare their protective effects against COVID-19 among healthcare workers (HCWs) during the Omicron outbreak in Taiwan.
Methods: Conducted from March 2021 to July 2023, this prospective observational study included healthy HCWs without prior COVID-19 immunization. Participants chose between adenovirus-vectored (AstraZeneca), mRNA (Moderna, BioNTech-Pfizer), and protein-based (Medigen, Novavax) vaccines. Blood samples were taken at multiple points to measure neutralizing antibody (nAb) titers, and adverse events (AEs) were recorded via questionnaires.
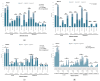
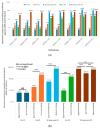
Results: Of 710 HCWs, 668 (94.1%) completed three doses, and 290 (40.8%) received a fourth dose during the Omicron outbreak. AEs were more common with AstraZeneca and Moderna vaccines, while Medigen caused fewer AEs. Initial nAb titers were highest with Moderna but waned over time regardless of the vaccine. Booster doses significantly increased nAb titers, with the highest levels observed in Moderna BA1 recipients. The fourth dose significantly reduced COVID-19 incidence, with Moderna BA1 being the most effective.
Conclusions: Regular booster doses, especially with mRNA and adjuvant-protein vaccines, effectively enhance nAb levels and reduce infection rates, providing critical protection for frontline HCWs during variant outbreaks.
Keywords: COVID-19; effectiveness; immunogenicity; reactogenicity; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- WHO Solidarity Trial Vaccines. [(accessed on 29 January 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/global-r....
-
- Ramasamy M.N., Minassian A.M., Ewer K.J., Flaxman A.L., Folegatti P.M., Owens D.R., Voysey M., Aley P.K., Angus B., Babbage G., et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of ChAdOx1 NCoV-19 Vaccine Administered in a Prime-Boost Regimen in Young and Old Adults (COV002): A Single-Blind, Randomised, Controlled, Phase 2/3 Trial. Lancet. 2021;396:1979–1993. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(20)32466-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Voysey M., Clemens S.A.C., Madhi S.A., Weckx L.Y., Folegatti P.M., Aley P.K., Angus B., Baillie V.L., Barnabas S.L., Bhorat Q.E., et al. Safety and Efficacy of the ChAdOx1 NCoV-19 Vaccine (AZD1222) against SARS-CoV-2: An Interim Analysis of Four Randomised Controlled Trials in Brazil, South Africa, and the UK. Lancet. 2021;397:99–111. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(20)32661-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

