Varicella-Zoster Disease of the Central Nervous System in Immunocompetent Children: Case Series and a Scoping Review
- PMID: 39340116
- PMCID: PMC11435507
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines12091086
Varicella-Zoster Disease of the Central Nervous System in Immunocompetent Children: Case Series and a Scoping Review
Abstract
Background: Varicella-Zoster Virus (VZV) is characterized by its ability to enter a dormant state within the body. When the wild or vaccine virus reactivates, it can lead to herpes zoster (HZ), which infrequently manifests as a neuroinfection.
Objectives: The aim of the study was to analyze the clinical manifestations and outcomes associated with VZV reactivation in the CNS in immunocompetent children.
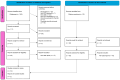
Methods: We searched medical databases for case reports using the keywords "zoster", "meningitis", "encephalitis", and "immunocompetent". The inclusion criteria were age below 18 years, any gender, race, and ethnicity, no features or history of immunodeficiency, and confirmation of VZV reactivation through the detection of VZV DNA in the CSF. Patients were categorized into two groups: children experiencing the reactivation of the wild virus and children with the vaccine strain virus.
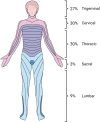
Results: The cohort included six children hospitalized in our hospital and 49 children reported in the literature. In 37 (67%), a wild-type virus was detected, while in 18 (33%), an infection was caused by the vaccine strain. There were no differences in the clinical presentation between the two groups. A typical rash was observed in 32 (58%) children. Approximately 41 of the 55 children (75%) received antiviral treatment. Four patients experienced complications.
Conclusions: Neither a history of VZV immunization nor the absence of a skin rash can definitively exclude VZV meningitis. It is important to note that any seemingly healthy child, regardless of recognized risk factors, could develop HZ meningitis.
Keywords: VZV; encephalitis; immunocompetent; meningitis; varicella; zoster.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Varicella-Zoster Virus Meningitis and Encephalitis: An Understated Cause of Central Nervous System Infections.Cureus. 2020 Nov 20;12(11):e11583. doi: 10.7759/cureus.11583. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 33364107 Free PMC article.
-
Primary varicella zoster infection compared to varicella vaccine reactivation associated meningitis in immunocompetent children.J Paediatr Child Health. 2021 Jan;57(1):19-25. doi: 10.1111/jpc.15303. Epub 2020 Dec 8. J Paediatr Child Health. 2021. PMID: 33295075 Review.
-
A Rare Case of Varicella-Zoster Virus Meningitis With High Intracranial Pressure in an Immunocompetent Adult.Cureus. 2024 Jan 17;16(1):e52437. doi: 10.7759/cureus.52437. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38370997 Free PMC article.
-
Meningitis without Rash after Reactivation of Varicella Vaccine Strain in a 12-Year-Old Immunocompetent Boy.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Jan 30;11(2):309. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11020309. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36851187 Free PMC article.
-
Encephalitis due to herpes zoster without rash in an immunocompetent 12-year-old girl: case report and review of the literature.BMC Pediatr. 2020 Jul 18;20(1):348. doi: 10.1186/s12887-020-02244-0. BMC Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32682414 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metagenomic next-generation sequencing of cerebrospinal fluid: a diagnostic approach for varicella zoster virus-related encephalitis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Dec 24;14:1509630. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1509630. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39776437 Free PMC article.
-
Herpes Zoster Oticus With Facial Palsy and Hearing Loss: A Case Report of Ramsay Hunt Syndrome in an Older Patient.Clin Case Rep. 2025 Feb 24;13(3):e70272. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.70272. eCollection 2025 Mar. Clin Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40012934 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

