Yap methylation-induced FGL1 expression suppresses anti-tumor immunity and promotes tumor progression in KRAS-driven lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 39340215
- PMCID: PMC12015977
- DOI: 10.1002/cac2.12609
Yap methylation-induced FGL1 expression suppresses anti-tumor immunity and promotes tumor progression in KRAS-driven lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: Despite significant strides in lung cancer immunotherapy, the response rates for Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (KRAS)-driven lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) patients remain limited. Fibrinogen-like protein 1 (FGL1) is a newly identified immune checkpoint target, and the study of related resistance mechanisms is crucial for improving the treatment outcomes of LUAD patients. This study aimed to elucidate the potential mechanism by which FGL1 regulates the tumor microenvironment in KRAS-mutated cancer.
Methods: The expression levels of FGL1 and SET1 histone methyltransferase (SET1A) in lung cancer were assessed using public databases and clinical samples. Lentiviruses were constructed for transduction to overexpress or silence FGL1 in lung cancer cells and mouse models. The effects of FGL1 and Yes-associated protein (Yap) on the immunoreactivity of cytotoxic T cells in tumor tissues were evaluated using immunofluorescence staining and flow cytometry. Chromatin immunoprecipitation and dual luciferase reporter assays were used to study the SET1A-directed transcriptional program.
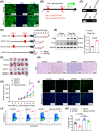
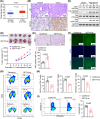
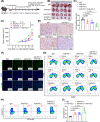
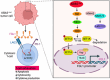
Results: Upregulation of FGL1 expression in KRAS-mutated cancer was inversely correlated with the infiltration of CD8+ T cells. Mechanistically, KRAS activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2), which subsequently phosphorylated SET1A and increased its stability and nuclear localization. SET1A-mediated methylation of Yap led to Yap sequestration in the nucleus, thereby promoting Yap-induced transcription of FGL1 and immune evasion in KRAS-driven LUAD. Notably, dual blockade of programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) and FGL1 further increased the therapeutic efficacy of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in LUAD patients.
Conclusion: FGL1 could be used as a diagnostic biomarker of KRAS-mutated lung cancer, and targeting the Yap-FGL1 axis could increase the efficacy of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy.
Keywords: FGL1; KRAS‐driven; SET1A; Yap; immune evasion; lung adenocarcinoma; methylation.
© 2024 The Author(s). Cancer Communications published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Sun Yat‐sen University Cancer Center.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
CREPT promotes LUAD progression by enhancing the CDK9 and RNAPII assembly to promote ERK-driven gene transcription.Theranostics. 2025 Jul 25;15(16):8337-8359. doi: 10.7150/thno.115572. eCollection 2025. Theranostics. 2025. PMID: 40860160 Free PMC article.
-
m6A-induced TRIB3 regulates Hippo pathway through interacting with LATS1 to promote the progression of lung adenocarcinoma.J Cell Physiol. 2024 May;239(5):e31220. doi: 10.1002/jcp.31220. Epub 2024 Feb 19. J Cell Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38372068
-
Trametinib sensitizes KRAS-mutant lung adenocarcinoma tumors to PD-1/PD-L1 axis blockade via Id1 downregulation.Mol Cancer. 2024 Apr 20;23(1):78. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-01991-3. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38643157 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Pathway, Yes-Associated Protein (YAP) and the Regulation of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC).Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 5;20(15):3821. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153821. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31387256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of B cell immunity in lung adenocarcinoma.Genes Immun. 2025 Jun;26(3):253-265. doi: 10.1038/s41435-025-00331-9. Epub 2025 May 13. Genes Immun. 2025. PMID: 40360749 Review.
Cited by
-
Posttranslational modifications of YAP/TAZ: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 Jul 17;30(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s11658-025-00760-4. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40676528 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RAF1 promotes anlotinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by inhibiting apoptosis.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2025 Apr 14;151(4):138. doi: 10.1007/s00432-025-06175-0. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40227502 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-secreted RGS17 impairs CD8 + T cell function in lung adenocarcinoma through affecting glucose metabolism mediated by PI3K/AKT pathway.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jul 8;16(1):1281. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02850-3. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40627213 Free PMC article.
-
Current status of KRAS G12C inhibitors in NSCLC and the potential for combination with anti-PD-(L)1 therapy: a systematic review.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 15;16:1509173. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1509173. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40303413 Free PMC article.
-
The role of histone methyltransferases in therapeutic resistance of NSCLC.Epigenetics. 2025 Dec;20(1):2536786. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2025.2536786. Epub 2025 Jul 23. Epigenetics. 2025. PMID: 40701777 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82002450/National Natural Science Foundation of China Youth Project
- 2020xkjT023/Basic and Clinical Collaboration Enhancement Program of Anhui Medical University
- 2022AH030081/The Research Program for Higher Education Institutions in Anhui Province
- 2023AH050656/The Research Program for Higher Education Institutions in Anhui Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

