Quantifying brain development in the HEALthy Brain and Child Development (HBCD) Study: The magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy protocol
- PMID: 39341120
- PMCID: PMC11466640
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dcn.2024.101452
Quantifying brain development in the HEALthy Brain and Child Development (HBCD) Study: The magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy protocol
Abstract
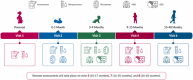
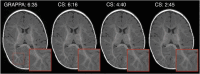
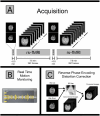
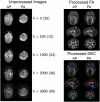
The HEALthy Brain and Child Development (HBCD) Study, a multi-site prospective longitudinal cohort study, will examine human brain, cognitive, behavioral, social, and emotional development beginning prenatally and planned through early childhood. The acquisition of multimodal magnetic resonance-based brain development data is central to the study's core protocol. However, application of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) methods in this population is complicated by technical challenges and difficulties of imaging in early life. Overcoming these challenges requires an innovative and harmonized approach, combining age-appropriate acquisition protocols together with specialized pediatric neuroimaging strategies. The HBCD MRI Working Group aimed to establish a core acquisition protocol for all 27 HBCD Study recruitment sites to measure brain structure, function, microstructure, and metabolites. Acquisition parameters of individual modalities have been matched across MRI scanner platforms for harmonized acquisitions and state-of-the-art technologies are employed to enable faster and motion-robust imaging. Here, we provide an overview of the HBCD MRI protocol, including decisions of individual modalities and preliminary data. The result will be an unparalleled resource for examining early neurodevelopment which enables the larger scientific community to assess normative trajectories from birth through childhood and to examine the genetic, biological, and environmental factors that help shape the developing brain.
Keywords: Development; HBCD; Infant; MRI; MRS; Protocol.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. Tobias Kober and Tom Hilbert are employees of Siemens Healthineers International AG, Switzerland. Yulin Chang is an employee of Siemens Medical Solutions USA Inc. Dan Rettmann and Ralph Noeske are employed by GE HealthCare. Guillaume Gilbert, Yansong Zhao, Sandeep Ganji, and Maarten Versluis are employed by Philips Healthcare. Carina Lucena, Lucky Heisler-Roman, and Dhruman Goradia are employed by PrimeNeuro Inc. Under a license agreement between Philips and the Johns Hopkins University, Dr. van Zijl and the University are entitled to fees related to an imaging device used in the study discussed for publication. Dr. van Zijl also is a paid lecturer for Philips and receives research support from Philips. This arrangement has been reviewed and approved by the Johns Hopkins University in accordance with its conflict of interest policies. Damien Fair is a patent holder on the Framwise Integrated Real-Time Motion Monitoring (FIRMM) software. He is also a co-founder of Turing Medical Technologies, Inc. The nature of this financial interest and the design of the study have been reviewed by two committees at the University of Minnesota. They have put in place a plan to help ensure that this research is not affected by the financial interest. All other authors report no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Alex A.M., Aguate F., Botteron K., Buss C., Chong Y.S., Dager S.R., Donald K.A., Entringer S., Fair D.A., Fortier M.V., Gaab N., Gilmore J.H., Girault J.B., Graham A.M., Groenewold N.A., Hazlett H., Lin W., Meaney M.J., Piven J., Qiu A., Rasmussen J.M., Roos A., Schultz R.T., Skeide M.A., Stein D.J., Styner M., Thompson P.M., Turesky T.K., Wadhwa P.D., Zar H.J., Zollei L., de Los Campos G., Knickmeyer R.C., group EO A global multicohort study to map subcortical brain development and cognition in infancy and early childhood. Nat. Neurosci. 2024;27(1):176–186. doi: 10.1038/s41593-023-01501-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alexander A.L., Hurley S.A., Samsonov A.A., Adluru N., Hosseinbor A.P., Mossahebi P., Tromp do P.M., Zakszewski E., Field A.S. Characterization of cerebral white matter properties using quantitative magnetic resonance imaging stains. Brain Connect. 2011;1(6):423–446. doi: 10.1089/brain.2011.0071. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 EB023963/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DA055330/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055338/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055366/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055359/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055371/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD103537/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055342/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055365/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K99 AG080084/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055316/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P41 EB031771/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055347/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R00 AG062230/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055349/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055370/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055358/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055369/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB032788/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055357/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055350/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055361/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055367/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002369/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055352/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055362/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 EB033516/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055344/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055355/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DA055325/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055353/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055363/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055322/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055354/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055352/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB016089/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055360/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States

