Arntl-induced upregulation of DUSP1 inhibits tumor progression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by inactivating ERK signaling
- PMID: 39341782
- PMCID: PMC11445925
- DOI: 10.1080/15384047.2024.2408042
Arntl-induced upregulation of DUSP1 inhibits tumor progression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by inactivating ERK signaling
Abstract
Background: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is a primary histological type of esophageal carcinoma with high morbidity. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like (ARNTL) is a circadian clock gene associated with the progression of multiple tumors. However, its roles and mechanisms in ESCC remain unknown.
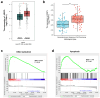
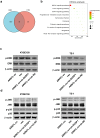
Methods: ARNTL expression was analyzed using TCGA database and detected using qRT-PCR, and ARNTL-related pathways were analyzed through GSEA. Cell functional behaviors were assessed in vitro by measuring cell viability, proliferation, and apoptosis. Cell growth in the murine model was investigated through xenograft model and immunofluorescence assays of PCNA and Ki67. The downstream targets of ARNTL were analyzed through sequencing and identified via luciferase report, ChIP, and RNA pull-down analyses. Dual-specificity protein phosphatase-1 (DUSP1) expression was analyzed using GEO datasets and measured using qRT-PCR and western blotting. Protein expression was examined via western blotting.
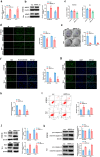
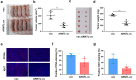
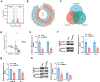
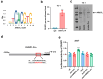
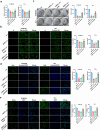
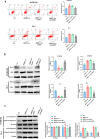
Results: ARNTL expression was decreased in esophageal carcinoma and associated with histological types, and elevated expression of ARNTL repressed ESCC cell viability and proliferation and facilitated cell apoptosis. ARNTL upregulation reduced tumor cell growth in murine models and decreased PCNA and Ki67 levels. Furthermore, DUSP1 was downregulated upon ARNTL silencing in ESCC. ARNTL could bind and positively regulate DUSP1 transcription. Additionally, DUSP1 silencing reversed the influences of ARNTL upregulation on cell viability, proliferation, and apoptosis in ESCC cells. ARNTL attenuated the activation of the ERK signaling by decreasing ERK phosphorylation through upregulation of DUSP1.
Conclusion: ARNTL hinders cell growth and contributes to cell apoptosis by inactivating ERK signaling through transcriptional upregulation of DUSP1 in ESCC.
Keywords: ARNTL; DUSP1; ERK; Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; apoptosis.
Plain language summary
• ARNTL is differentially expressed in ESCC and associated with cell apoptosis.• ARNTL augments cell apoptosis.• ARNTL increases DUSP1 transcription.• ARNTL inhibits activation of the ERK signaling by upregulating DUSP1.• DUSP1 silencing reverses the effects of ARNTL in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
