Investigating the association between the triglyceride-glucose index and peripheral artery disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39341836
- PMCID: PMC11438956
- DOI: 10.1038/s41387-024-00341-y
Investigating the association between the triglyceride-glucose index and peripheral artery disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a common disease associated with atherosclerosis, leading to significant mortality and morbidity worldwide. Our study focuses on the association between insulin resistance (IR) and PAD, specifically investigating the triglyceride-glucose index (TyG) as a potential surrogate marker of IR in the context of PAD by pooling the existing studies on this topic.
Methods: Online databases, including PubMed, Embase, Scopus, and the Web of Science, were searched to find the studies comparing the TyG index in PAD vs. control, reporting the TyG index among PAD severities, and assessing the association of increase in TyG with PAD prevalence. Random-effect meta-analysis was performed to calculate the standardized mean difference (SMD) and 95% confidence interval (CI) for TyG level comparison and to calculate pooled odds ratio (ORs) for a 1-unit increase in TyG and higher vs. lower quartile/tertile of TyG association with PAD.
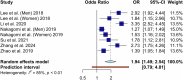
Results: In the final review, 22 studies comprising 73,168 cases were included. Random-effect meta-analysis showed that patients with PAD had significantly higher levels of the TyG index compared with controls (SMD 0.76, 95%CI 0.65-0.88, P < 0.001). Also, higher severities of PAD were associated with higher TyG levels (SMD 0.48, 95%CI 0.22-0.74, P = 0.0003). Additionally, a 1-unit increase in TyG was associated with a 60% increase in odds of PAD (OR 1.60, 95%CI 1.41-1.80, P < 0.001). Finally, the highest quartile (Q4) of TyG had significantly higher odds of PAD compared to Q1 (OR 1.94, 95%CI 1.49-2.54, P < 0.001).
Conclusion: Our meta-analysis has identified a significant association between TyG levels and PAD and its severity. These findings not only contribute to our understanding of the role of IR in PAD pathology but also offer clinicians an exact index for evaluating PAD risk and its complications. This could potentially lead to more effective prevention and management strategies in the future.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Song P, Fang Z, Wang H, Cai Y, Rahimi K, Zhu Y, et al. Global and regional prevalence, burden, and risk factors for carotid atherosclerosis: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and modelling study. Lancet Glob Health. 2020;8:e721–e9. - PubMed
-
- Norgren L, Hiatt WR, Dormandy JA, Nehler MR, Harris KA, Fowkes FG, et al. Inter-Society Consensus for the Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease (TASC II). J Vasc Surg. 2007;45:S5–67. Suppl S - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

