Amyloid precursor protein as a fibrosis marker in infants with biliary atresia
- PMID: 39341941
- PMCID: PMC12119347
- DOI: 10.1038/s41390-024-03582-w
Amyloid precursor protein as a fibrosis marker in infants with biliary atresia
Abstract
Background: Biliary atresia (BA) is a rare condition of unknown origin in newborns with jaundice. In BA bile ducts are non-functional, causing neonatal cholestasis and following liver fibrosis and failure.
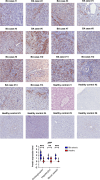
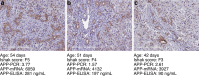
Methods: This retrospective study included liver biopsies of 14 infants with BA aged [mean ± SD] 63 ± 23 days. Patients were grouped according to the clinical course (jaundice-free vs recurrent jaundice vs required liver transplantation or liver fibrosis (Ishak fibrosis score)) and followed for 1.61-5.64 years (mean 4.03). Transcriptome profiles were assessed using a panel of 768 fibrosis-specific genes, reanalyzed via qRT-PCR, and confirmed via immunostaining. Plasma from an additional 30 BA infants and 10 age-matched controls were used for amyloid precursor protein (APP) quantification by ELISA.
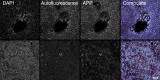
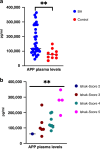
Results: Different clinical outcome groups showed a homogeneous mRNA expression. Altered amyloid-metabolism-related gene expression was found between cases with Ishak fibrosis score greater than 4. Immunostaining confirmed a distinct presence of APP in the livers of all BA subjects. APP plasma levels were higher in BA than in age-matched controls and correlated with the histological fibrosis grade.
Conclusions: These results suggest that amyloidosis may contribute to BA and liver fibrosis, indicating that APP could serve as a potential liquid biomarker for these conditions.
Impact: Biliary atresia patients with higher fibrosis scores according to Ishak have higher hepatic expression of amyloid-related genes while amyloid precursor protein accumulates in the liver and increases in the circulation. After a recent study revealed beta-amyloid deposition as a mechanism potentially involved in biliary atresia, we were able to correlate amyloid-metabolism-related transcript levels as well as amyloid precursor protein tissue and plasma levels with the degree of hepatic fibrosis. These findings suggest that amyloid precursor protein is a fibrosis marker in infants with biliary atresia, reinforcing the role of amyloid metabolism in the pathogenesis of this serious disease.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Consent for publication: All subjects included in this study or their parents gave written informed consent.
Figures

References
-
- Livesey, E. et al. Epidemiology of biliary atresia in England and Wales (1999–2006). Arch. Dis. Child Fetal Neonatal Ed.94, F451–F455 (2009). - PubMed
-
- The, N. S. et al. National Birth Defects Prevention Study. Risk factors for isolated biliary atresia, National Birth Defects Prevention Study, 1997–2002. Am. J. Med. Genet. A.143A, 2274–2284 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Medappil, N. et al. Kasai portoenterostomy for biliary atresia - surgical precautions for better outcomes. J. Pediatr. Surg.54, 868–869 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

