Importance of biopsy sample length for cancer diagnosis during trans-perineal prostate biopsy
- PMID: 39342172
- PMCID: PMC11438266
- DOI: 10.1186/s12894-024-01596-4
Importance of biopsy sample length for cancer diagnosis during trans-perineal prostate biopsy
Abstract
Objective: To identify the factors that determine the minimum length of biopsy sample required for accurate diagnosis.
Materials and methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on 1202 cases that underwent rectal ultrasound-guided trans-perineal prostate biopsy (TPB) with standardized biopsy surgical procedures and pathological evaluation. Logistic regression correlation analysis and the imbalance between groups was eliminated by propensity score matching of patients' own factors between groups (positive group and negative group). ROC curve optimal threshold analysis were performed to identify the independent factors associated with cancer detection rate and the minimum length of biopsy sample required for accurate diagnosis.
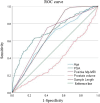
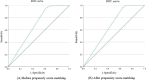
Results: The study included 1202 cases that underwent standardized 8-18 needle initial puncture biopsies from June 2020 to October 2023. The cancer detection rate was 40.02% (481/1202), with Gleason scores of 6, 7, 8, 9, and 10 in 164, 134, 107, 67, and 9 patients, respectively. The percentage of patients with clinical significance (International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) ≥ 2) was 65.90% (317/481). Multivariate analysis showed that age,prostate-specific antigen(PSA), prostate volume,positive multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging (mp-MRI) and length of biopsy samples were significant factors (P < 0.05)。Interestingly, biopsy sample length did not correlate with the prostate volume (Pearson correlation P = 0.069). ROC curve analysis: The area under the curve AUC for sample length were 0.674 and 0.664 at before and after propensity score matching,respectively; the optimal thresholds were 12.25 mm and 11.00mm at before and after propensity score matching,respectively.
Conclusion: The independent predictors of cancer detection rate during TPB are age, PSA, prostate volume, positive mp-MRI, and sample length. Among these, sample length is the most critical indicator affecting puncture quality, and the minimum value of biopsy sample length to be obtained is 11.00mm.
Keywords: Biopsy sample length; Diagnosis; Propensity score matching; Prostate tumor; Trans-perineal biopsy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Enzinger B, Pfitzinger PL, Ebner B, et al. Common errors, pitfalls, and management of complications of prostate biopsy : the most common diagnostic and procedural challenges of transrectal fusion prostate biopsy in the initial diagnosis of clinically significant prostate cancer. Urologie. 2023;62(5):479–86. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 2022KY1332;2021-3-022/This work was supported by grants from the Zhejiang Provincial Medical and Health Program Project (2022KY1332), Zhejiang Jinhua City (Social Development Category) Major Science and Technology Research Program Project (2021-3-022)
- 2022KY1332;2021-3-022/This work was supported by grants from the Zhejiang Provincial Medical and Health Program Project (2022KY1332), Zhejiang Jinhua City (Social Development Category) Major Science and Technology Research Program Project (2021-3-022)
- 2022KY1332;2021-3-022/This work was supported by grants from the Zhejiang Provincial Medical and Health Program Project (2022KY1332), Zhejiang Jinhua City (Social Development Category) Major Science and Technology Research Program Project (2021-3-022)
- 2022KY1332;2021-3-022/This work was supported by grants from the Zhejiang Provincial Medical and Health Program Project (2022KY1332), Zhejiang Jinhua City (Social Development Category) Major Science and Technology Research Program Project (2021-3-022)
- 2022KY1332;2021-3-022/This work was supported by grants from the Zhejiang Provincial Medical and Health Program Project (2022KY1332), Zhejiang Jinhua City (Social Development Category) Major Science and Technology Research Program Project (2021-3-022)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

