Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and cardiovascular risk: a comprehensive review
- PMID: 39342178
- PMCID: PMC11439309
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-024-02434-5
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and cardiovascular risk: a comprehensive review
Abstract
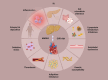
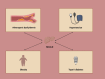
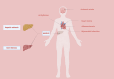
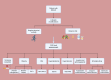
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), previously termed nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), poses a significant global health challenge due to its increasing prevalence and strong association with cardiovascular disease (CVD). This comprehensive review summarizes the current knowledge on the MASLD-CVD relationship, compares analysis of how different terminologies for fatty liver disease affect cardiovascular (CV) risk assessment using different diagnostic criteria, explores the pathophysiological mechanisms connecting MASLD to CVD, the influence of MASLD on traditional CV risk factors, the role of noninvasive imaging techniques and biomarkers in the assessment of CV risk in patients with MASLD, and the implications for clinical management and prevention strategies. By incorporating current research and clinical guidelines, this review provides a comprehensive overview of the complex interplay between MASLD and cardiovascular health.
Keywords: Cardiovascular risk; Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease; Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Targher G, Byrne CD, Tilg H. MASLD: a systemic metabolic disorder with cardiovascular and malignant complications. Gut. 2024;73(4):691–702. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

