Serum salicylic acid levels in children with Kawasaki disease
- PMID: 39342233
- PMCID: PMC11438225
- DOI: 10.1186/s12887-024-05100-7
Serum salicylic acid levels in children with Kawasaki disease
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to clarify serum salicylic acid (SA) levels in patients with Kawasaki disease (KD) after the administration of moderate-dose acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) and their relationship with the therapeutic effect.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed the clinical data of 142 children with KD. We measured serum SA trough levels during the acute and recovery periods and determined their relationship with clinical and laboratory parameters.
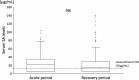
Results: The median age of patients was 2.4 years. Thirty-one patients had incomplete KD, 29 were intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) non-responders, and one patient had coronary artery lesions. The median ASA dose was 49.7 mg/kg/day. The median serum SA level was 22 µg/mL in the acute period and 15 µg/mL in the recovery period, with 45 (33%) in the acute period and 60 (44%) in the recovery period below the limit of measurement (< 10 µg/mL). Serum SA levels during the recovery period were significantly lower in patients who received steroids. There were no significant differences in IVIG responsiveness based on serum SA levels.
Conclusions: Serum SA trough levels in KD patients treated with moderate-dose ASA were highly variable and did not reach sufficient levels. Serum SA levels were not associated with IVIG responsiveness.
Keywords: Acetylsalicylic acid; Intravenous immunoglobulin; Kawasaki disease; Serum salicylic acid level; Steroid.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Research Committee of the Japanese Society of Pediatric Cardiology, Cardiac Surgery Committee for Development of Guidelines for Medical Treatment of Acute Kawasaki Disease. Guidelines for medical treatment of acute Kawasaki disease: report of the Research Committee of the Japanese Society of Pediatric Cardiology and Cardiac surgery (2012 revised version). Pediatr Int. 2014;56:135–58. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Research Committee of the Japanese Society of Pediatric Cardiology; Cardiac Surgery Committee for Development of Guidelines for Medical Treatment of Acute Kawasaki Disease. Guidelines for medical treatment of acute Kawasaki disease (2020 revised version). J Pediatr Cardiol Card Surg. 2021;5:41–73. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

