Altered oxidant and antioxidant levels are associated with vascular stiffness and diabetic kidney disease in type 1 diabetes after exposure to acute and chronic hyperglycemia
- PMID: 39342285
- PMCID: PMC11439198
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-024-02427-4
Altered oxidant and antioxidant levels are associated with vascular stiffness and diabetic kidney disease in type 1 diabetes after exposure to acute and chronic hyperglycemia
Abstract
Background: Hyperglycemia-induced oxidative stress is a well-established pathological mediator of vascular complications in diabetes. We assessed plasma oxidant and antioxidant levels in response to acute and chronic hyperglycemia in relation to vascular stiffness and varying degrees of kidney disease in type 1 diabetes individuals.
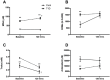
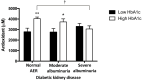
Methods: The acute hyperglycemia study included 22 type 1 diabetic individuals with normal albumin excretion rate (AER) and 13 non-diabetic controls. These individuals received an acute glucose challenge during a 120-minute hyperglycemic clamp. The chronic hyperglycemia study included 118 type 1 diabetic individuals with chronically low (n = 60) or high (n = 58) HbA1c concentrations and varying degrees of diabetic kidney disease (DKD) classified as normal, moderate, or severe albuminuria (AER). Levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), reactive oxygen metabolites (ROMs), total antioxidant capacity (TAC), biological antioxidant potential (BAP) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) were measured from plasma or serum samples in the FinnDiane study.
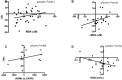
Results: Levels of MDA (p < 0.01) and ROMs (p < 0.01) were elevated in type 1 diabetes individuals compared to non-diabetic controls at baseline. Acute hyperglycemia further increased MDA levels (p < 0.05) and sustained the elevation of ROMs in type 1 diabetes individuals. Acute hyperglycemic challenge impaired TAC in both non-diabetic (p < 0.05) and type 1 diabetes (p < 0.01) individuals compared to baseline whereas BAP was increased (p < 0.05) with no difference observed in non-diabetic controls. There was a positive association between high circulating MDA and AIx (r2 = 0.611, p = 0.05), and between delta ROMs and delta AIx (r2 = 0.955, p = 0.014) in combined analysis of individuals with type 1 diabetes and non-diabetic controls. Type 1 diabetes individuals with varying status of DKD, showed elevated levels of ROMs in those with high HbA1c compared to their counterpart with low HbA1c (p < 0.05). Individuals with severe albuminuria showed elevated ROM levels (p < 0.01) and depressed antioxidant capacity (p < 0.01) compared to those with normal AER of comparable HbA1c concentrations.
Conclusions: Biomarkers of oxidative stress are associated with vascular stiffness and DKD following acute and chronic hyperglycemic exposure and may provide added value to HbA1c in understanding disease pathology, predicting risk and assessing the status of secondary complications of type 1 diabetes.
Keywords: Antioxidant capacity; Arterial stiffness; Diabetes; Diabetic kidney disease; Hyperglycemia; Oxidative stress.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Jha JC, Gray SP, Barit D, Okabe J, El-Osta A, Namikoshi T, Thallas-Bonke V, Wingler K, Szyndralewiez C, Heitz F, Touyz RM, Cooper ME, Schmidt HH, Jandeleit-Dahm KA. Genetic targeting or pharmacologic inhibition of NADPH oxidase nox4 provides renoprotection in long-term diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014;25:1237–54. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Menon BB, Pathare NA. An in vitro evaluation of antibiotic combinations for urinary tract infections in patients with diabetes mellitus. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2004;47:565–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

