Association between high-density lipoprotein-related inflammation index and periodontitis: insights from NHANES 2009-2014
- PMID: 39342327
- PMCID: PMC11439298
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-024-02312-9
Association between high-density lipoprotein-related inflammation index and periodontitis: insights from NHANES 2009-2014
Abstract
Background: Periodontitis, a persistent inflammatory condition, significantly impairs individuals' overall quality of life. Lymphocyte-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (LHR), monocyte-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (MHR), neutrophil-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (NHR), and platelet-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (PHR) are new convenient and economical biomarkers. However, whether the above high-density lipoprotein-related inflammatory biomarkers are associated with periodontitis has rarely been investigated. Therefore, the research endeavor focused on uncovering potential relationships.
Methods: The research encompassed a diverse and extensive sample, comprising 9,470 participants, selected from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey spanning the years 2009 to 2014. The association between high-density lipoprotein-related inflammatory biomarkers and periodontitis was explored utilizing a multivariable logistic regression model with weighted analysis. Additionally, the study employed smoothed curve fitting to explore potential nonlinear relationships. Further stratified analyses and interaction tests were performed.
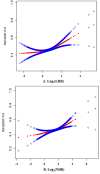
Results: This study indicated no apparent association between MHR and PHR with periodontitis, whereas LHR and NHR demonstrated a statistically significant positive relationship with the prevalence of periodontitis. In the fully adjusted model, participants belonging to the highest tertile of both LHR and NHR showed a notably higher likelihood of having periodontitis compared to those in the lowest tertile (LHR: OR = 1.22, 95% CI: 1.06, 1.39; NHR: OR = 1.27, 95% CI: 1.09, 1.49). Furthermore, smooth curve fitting was employed to investigate the potential nonlinear relationship between LHR, NHR, and periodontitis. The results indicated that there was a significant increase in the occurrence of periodontitis when Log2 (LHR) exceeded 1.01 and Log2(NHR) surpassed 2.16 (Log2(LHR): OR = 1.42; 95% CI: 1.19, 1.69; Log2(NHR): OR = 1.40; 95% CI: 1.15, 1.71). The subgroup analysis revealed that the associations between periodontitis and either LHR or NHR, separately, were more pronounced among individuals under the age of 50 and those without hypertension.
Conclusions: This cross-sectional study revealed a positive relationship between LHR、NHR and periodontitis, particularly when these indicators exceeded their thresholds. LHR and NHR may serve as potential inflammatory markers for identifying periodontitis, thereby facilitating early warning for both patients and dentists, and enabling early intervention in the oral environment. Besides, extensive prospective cohort investigations are essential to confirm and solidify this observation.
Keywords: High-density lipoprotein-related inflammatory biomarkers; NHANES; Periodontitis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Association of High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol-Based Inflammatory Markers With MASLD and Significant Liver Fibrosis in US Adults: Insights From NHANES 2017-2020.Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2025 Jun 16;16(8):e00873. doi: 10.14309/ctg.0000000000000873. eCollection 2025 Aug 1. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40522334 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Three Composite Inflammatory and Lipid Metabolism Indicators With Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Syndrome: A Cross-Sectional Study Based on NHANES 1999-2020.Mediators Inflamm. 2025 May 8;2025:6691516. doi: 10.1155/mi/6691516. eCollection 2025. Mediators Inflamm. 2025. PMID: 40376312 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphocyte-derived and lipoprotein-derived inflammatory ratios as biomarkers in bipolar disorder type I: Characteristics, predictive values, and influence of current psychopharmacological treatments.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2025 Jan;171:107209. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2024.107209. Epub 2024 Oct 15. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2025. PMID: 39442230
-
Investigation of systemic immune-inflammation index, neutrophil/high-density lipoprotein ratio, lymphocyte/high-density lipoprotein ratio, and monocyte/high-density lipoprotein ratio as indicators of inflammation in patients with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.Front Psychiatry. 2022 Jul 26;13:941728. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.941728. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35958647 Free PMC article.
-
The role of systemic inflammatory indices in predicting atrial fibrillation and its complications: a narrative review.Curr Med Res Opin. 2024 Oct;40(10):1657-1666. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2024.2397074. Epub 2024 Sep 2. Curr Med Res Opin. 2024. PMID: 39210892 Review.
Cited by
-
Association between systemic inflammation indicators and psoriasis: a cross-sectional study from NHANES.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 13;16:1556487. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1556487. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40181962 Free PMC article.
-
Association of neutrophil to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio with overactive bladder: a population-based study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 May 22;16:1541294. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1541294. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40475997 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet-to-high-density lipoprotein ratio (PHR) as a predictive biomarker for gastrointestinal cancers: evidence from NHANES.BMC Gastroenterol. 2025 Apr 27;25(1):302. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-03860-9. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40289098 Free PMC article.
-
Association of High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol-Based Inflammatory Markers With MASLD and Significant Liver Fibrosis in US Adults: Insights From NHANES 2017-2020.Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2025 Jun 16;16(8):e00873. doi: 10.14309/ctg.0000000000000873. eCollection 2025 Aug 1. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40522334 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Three Composite Inflammatory and Lipid Metabolism Indicators With Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Syndrome: A Cross-Sectional Study Based on NHANES 1999-2020.Mediators Inflamm. 2025 May 8;2025:6691516. doi: 10.1155/mi/6691516. eCollection 2025. Mediators Inflamm. 2025. PMID: 40376312 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Slots J. Periodontitis: facts, fallacies and the future. Periodontol 2000. 2017;75(1):7–23. - PubMed
-
- Tonetti MS, Van Dyke TE. Working group 1 of the joint EFP/AAP workshop. Periodontitis and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: consensus report of the Joint EFP/AAP Workshop on Periodontitis and systemic diseases. J Periodontol. 2013;84(4 Suppl):S24–29. - PubMed
-
- Herrera D, Sanz M, Shapira L, et al. Association between periodontal diseases and cardiovascular diseases, diabetes and respiratory diseases: Consensus report of the Joint Workshop by the European Federation of Periodontology (EFP) and the European arm of the World Organization of Family doctors (WONCA Europe). J Clin Periodontol. 2023;50(6):819–41. - PubMed
-
- Chen MX, Zhong YJ, Dong QQ, Wong HM, Wen YF. Global, regional, and national burden of severe periodontitis, 1990–2019: an analysis of the global burden of Disease Study 2019. J Clin Periodontol. 2021;48(9):1165–88. - PubMed
-
- Haas MJ, Mooradian AD. Regulation of high-density lipoprotein by inflammatory cytokines: establishing links between immune dysfunction and cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2010;26(2):90–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

