LYP regulates SLP76 and other adaptor proteins in T cells
- PMID: 39342392
- PMCID: PMC11438317
- DOI: 10.1186/s40659-024-00536-8
LYP regulates SLP76 and other adaptor proteins in T cells
Abstract
Background: The LYP tyrosine phosphatase presents a SNP (1858C > T) that increases the risk of developing autoimmune diseases such as type I diabetes and arthritis. It remains unclear how this SNP affects LYP function and promotes the development of these diseases. The scarce information about LYP substrates is in part responsible for the poor understanding of LYP function.
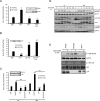
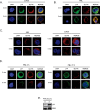
Results: In this study, we identify in T lymphocytes several adaptor proteins as potential substrates targeted by LYP, including FYB, SLP-76, HS-1, Vav, SKAP1 and SKAP2. We also show that LYP co-localizes with SLP76 in microclusters, upon TCR engagement.
Conclusions: These data indicate that LYP may modulate T cell activation by dephosphorylating several adaptor proteins, such as FYB, SLP-76, HS-1, Vav, SKAP1 and SKAP2 upon TCR engagement.
Keywords: FYB; LYP (lymphoid phosphatase); Protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP); SKAP2; SLP76; T-cell; T-cell receptor (TCR).
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Vang T, Miletic A V, Arimura Y, Tautz L, Rickert RC, Mustelin T. Protein tyrosine phosphatases in autoimmunity. 2008; 26:29–55. 10.1146/annurev.immunol.26.021607.090418 - PubMed
-
- Badour K, Zhang J, Shi F, Leng Y, Collins M, Siminovitch KA. Fyn and PTP-PEST-mediated regulation of Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome Protein (WASp) tyrosine phosphorylation is required for coupling T cell antigen receptor engagement to WASp effector function and T cell activation. J Exp Med. 2004;199(1):99–111. 10.1084/jem.20030976 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

