Reading the m6A-encoded epitranscriptomic information in development and diseases
- PMID: 39342406
- PMCID: PMC11439334
- DOI: 10.1186/s13578-024-01293-7
Reading the m6A-encoded epitranscriptomic information in development and diseases
Abstract
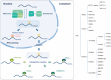
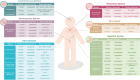
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) represents the most prevalent internal and reversible modification on RNAs. Different cell types display their unique m6A profiles, which are determined by the functions of m6A writers and erasers. M6A modifications lead to different outcomes such as decay, stabilization, or transport of the RNAs. The m6A-encoded epigenetic information is interpreted by m6A readers and their interacting proteins. M6A readers are essential for different biological processes, and the defects in m6A readers have been discovered in diverse diseases. Here, we review the latest advances in the roles of m6A readers in development and diseases. These recent studies not only highlight the importance of m6A readers in regulating cell fate transitions, but also point to the potential application of drugs targeting m6A readers in diseases.
Keywords: Cancers; Development; Diseases; m6A; m6A readers.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

