Parents' Willingness to Vaccinate Their Children Aged From 6 Months to Under 5 Years With COVID-19 Vaccines
- PMID: 39342435
- PMCID: PMC11982586
- DOI: 10.1177/00099228241281126
Parents' Willingness to Vaccinate Their Children Aged From 6 Months to Under 5 Years With COVID-19 Vaccines
Abstract
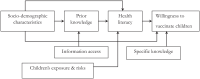
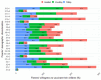
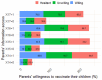
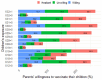
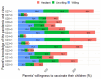
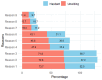
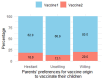
Despite strides in vaccinating priority groups against COVID-19, children under 5 years in Vietnam are still under-immunized, emphasizing a significant gap in prioritization. This study aimed to assess parental willingness to vaccinate children aged 6 months to under 5 years against COVID-19 in Vietnam and identify influential factors affecting this willingness. Data were collected via a survey of 5960 parents/guardians between May and June 2022. Multinomial logistic regression was employed to analyze the impact of various factors on parents' willingness to vaccinate their children, alongside investigating reasons for reluctance or refusal and preferences for vaccine origins. Approximately 50.5%, 30.2%, and 19.3% of parents were willing, hesitant, and unwilling to vaccinate their children, respectively. Primary reasons for reluctance included concerns about vaccine safety, efficacy, and the severity of the pandemic. The most preferred vaccines originated in the United States. Factors significantly influencing willingness included parents' age, knowledge of COVID-19 and vaccines, residency, education, perception of information sufficiency, children's comorbidities, and family members' vaccination status. Promoting child vaccination habits can boost COVID-19 immunization rates. Targeting hesitancy among parents of children with comorbidities is crucial. Enhancing parental knowledge and leveraging fully vaccinated family members are effective strategies.
Keywords: COVID-19 pandemic; COVID-19 vaccines; SARS-CoV-2 virus; children aged from 6 months to under 5 years; parents’ willingness to vaccinate their children; stratified surveys.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting InterestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Our World in Data. Share of people vaccinated against COVID-19. Published 2022. Accessed July 27, 2022. https://ourworldindata.org/covid-vaccinations.
-
- UNICEF. Children in Viet Nam. Published 2022. Accessed April 2022. https://www.unicef.org/vietnam/children-viet-nam
-
- Ministry of Health. Healthy children can become serious ill if infected with SARS-CoV-2. Published 2022. https://moh.gov.vn/hoat-dong-cua-dia-phuong/-/asset_publisher/gHbla8vOQD...
-
- Binh T. 19.2% of COVID-19 patients in our country are children, the mortality rate is low but cannot be subjective. Published 2022. Accessed April 2022. https://suckhoedoisong.vn/192-benh-nhan-covid-19-o-nuoc-ta-la-tre-em-ty-...
-
- Michelson A, Graaf MD. The 7 countries where kids under 5 years old are eligible for COVID-19 Vaccines, and how the roll-outs are shaping up. Published 2022. Accessed April, 2022. https://www.businessinsider.com/countries-where-kids-under-5-getting-cov...
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

