Optimizing the detection of N-nitrosamine mutagenicity in the Ames test
- PMID: 39343352
- PMCID: PMC12395388
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yrtph.2024.105709
Optimizing the detection of N-nitrosamine mutagenicity in the Ames test
Abstract
Accurately determining the mutagenicity of small-molecule N-nitrosamine drug impurities and nitrosamine drug substance-related impurities (NDSRIs) is critical to identifying mutagenic and cancer hazards. In the current study we have evaluated several approaches for enhancing assay sensitivity for evaluating the mutagenicity of N-nitrosamines in the bacterial reverse mutagenicity (Ames) test. Preincubation assays were conducted using five activation conditions: no exogenous metabolic activation and metabolic activation mixes employing both 10% and 30% liver S9 from hamsters and rats pretreated with inducers of enzymatic activity. In addition, preincubations were conducted for both 60 min and 30 min. These test variables were evaluated by testing 12 small-molecule N-nitrosamines and 17 NDSRIs for mutagenicity in Salmonella typhimurium tester strains TA98, TA100, TA1535, and TA1537, and Escherichia coli strain WP2 uvrA (pKM101). Eighteen of the 29 N-nitrosamine test substances tested positive under one or more of the testing conditions and all 18 positives could be detected by using tester strains TA1535 and WP2 uvrA (pKM101), preincubations of 30 min, and S9 mixes containing 30% hamster liver S9. In general, the conditions under which NDSRIs were mutagenic were similar to those found for small-molecule N-nitrosamines.
Keywords: Acceptable intake limit; Ames test; Carcinogenic potency categorization approach; Drug impurities; Hamster liver S9; Mutagenicity dose-response ranking; Nitrosamine drug substance-related impurities; Preincubation; Rat liver S9; Small-molecule N-Nitrosamines.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest To the best of their knowledge, the authors are not aware that they have any of the conflicts of interests listed in the Instructions to Authors.
Figures
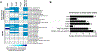

References
-
- Amacher DE, Paillet SC, 1983. The activation of procarcinogens to mutagens by cultured rat hepatocytes in the L5178Y/TK mutation assay. Mutat. Res. 113, 77–88. - PubMed
-
- Ames BN, McCann J, Yamasaki E, 1975. Methods for detecting carcinogens and mutagens with the Salmonella/mammalian-microsome mutagenicity test. Mutat. Res. 31, 347–364. - PubMed
-
- Andrews AW, Fornwald JA, Lijinsky W, 1980. Nitrosation and mutagenicity of some amine drugs. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 52, 237–244. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

