Dickkopf-related Protein 2 Promotes Hair Growth by Upregulating the Wnt/β-catenin Signaling Pathway in Human Dermal Papilla Cells
- PMID: 39343756
- PMCID: PMC11439980
- DOI: 10.5021/ad.23.128
Dickkopf-related Protein 2 Promotes Hair Growth by Upregulating the Wnt/β-catenin Signaling Pathway in Human Dermal Papilla Cells
Abstract
Background: The Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is crucial for the development, initiation, and growth of hair follicles (HFs). The Dickkopf-related protein (DKK) gene family encodes secreted proteins modulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Studies have reported that DKK1 promotes the regression of HFs and serves as a pathogenic mediator in male pattern baldness. However, the role of DKK2 on human hair growth has not yet been explored.
Objective: This study investigates direct effect of DKK2 on hair growth using human dermal papilla cell (DPC) cultures and ex vivo human HF organ cultures.
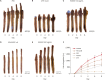
Methods: To elucidate the effect of DKK2 on hair growth, we examined the effect of recombinant human DKK2 (rhDKK2) treatment on cell viability, expression of mRNA and protein related to the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, and cell growth in cultured human DPCs. We also performed ex vivo organ culture of HFs with rhDKK2 and measured changes in hair shaft length for 8 days.
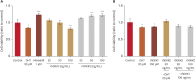
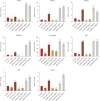
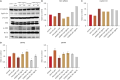
Results: Treatment with rhDKK2 led to a dose-dependent rise in the proliferation of human DPCs (p<0.05), reaching levels comparable to those induced by 1 μM minoxidil. Moreover, rhDKK2 increased the expression of Wnt/β-catenin target genes, phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase, and cyclin-D1; it also increased the BAX-to-Bcl-2 ratio and downregulated the bone morphogenetic protein 2 gene. In human HF organ cultures, relative to the control treatment, rhDKK2 treatment significantly increased hair shaft elongation (p<0.01).
Conclusion: Our results indicate that rhDKK2 could promote hair growth by facilitating the proliferation of human DPCs through activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
Keywords: Beta catenin; Dickkopf 2 protein, human; Hair follicle; Wnt signaling pathway.
© 2024 The Korean Dermatological Association and The Korean Society for Investigative Dermatology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Andl T, Reddy ST, Gaddapara T, Millar SE. WNT signals are required for the initiation of hair follicle development. Dev Cell. 2002;2:643–653. - PubMed
-
- Bafico A, Liu G, Yaniv A, Gazit A, Aaronson SA. Novel mechanism of Wnt signalling inhibition mediated by Dickkopf-1 interaction with LRP6/Arrow. Nat Cell Biol. 2001;3:683–686. - PubMed
-
- Semënov MV, Tamai K, Brott BK, Kühl M, Sokol S, He X. Head inducer Dickkopf-1 is a ligand for Wnt coreceptor LRP6. Curr Biol. 2001;11:951–961. - PubMed
-
- Kwack MH, Sung YK, Chung EJ, Im SU, Ahn JS, Kim MK, et al. Dihydrotestosterone-inducible dickkopf 1 from balding dermal papilla cells causes apoptosis in follicular keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 2008;128:262–269. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

