Ameliorating effects of natural herbal supplements against water-borne induced toxicity of heavy metals on Nile tilapia, (Oreochromis niloticus)
- PMID: 39343783
- PMCID: PMC11439952
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-72268-4
Ameliorating effects of natural herbal supplements against water-borne induced toxicity of heavy metals on Nile tilapia, (Oreochromis niloticus)
Abstract
The efficacy of herbal supplements in mitigating heavy metals (HMs) toxicity was investigated using a widely grown fish, the Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). The experiment was conducted over two phases: during the stress phase, the experimental fishes were exposed to sub-lethal concentrations of HMs, including lead, cadmium, zinc, and copper for 15 days; following which during the feeding phase, herbal supplements were given for 70 days to ameliorate their effects. Seven groups were established: the control negative group (CON-ve), control positive group (CON+ve, without any treatment), and five groups with supplementation of 1% turmeric (TUR), cinnamon (CIN), ginger (GIN), garlic (GAR), and their mixture (MIX), respectively. A total of 315 fishes were distributed evenly in experimental tanks (15 fishes per tank, in triplicates). The results revealed that exposure to HMs led to significant (p < 0.05) alterations in all the tested parameters, i.e., liver damage and growth reduction. The herbal supplements, especially the MIX groups, ameliorated the harmful effects of HMs and restored fish growth, digestibility, carcass composition, and liver health. In conclusion, the study demonstrated that the herbal supplements were effective in reducing the HMs-linked toxicity in Nile tilapia. Future studies pertaining to the mechanisms facilitated by the various herbal bioactive substances-linked tolerance to HMs in fishes are warranted.
Keywords: Growth; Heavy metal; Herbal supplement; Histopathology; Nile tilapia; Toxicity.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
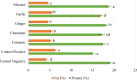
Figures



References
-
- Lee, J. Y. & Gao, Y. Review of the application of garlic, Allium sativum, in aquaculture. J. World Aquac. Soc.43(4), 447–458. 10.1111/j.1749-7345.2012.00581.x (2012).
-
- Naylor, R.L., Hardy, R.W., Buschmann, A.H. et al. 2021. A 20-year retrospective review of global aquaculture. Nature, 591, 551–563. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03308-6 - PubMed
-
- Ali, H. & Khan, E. What are heavy metals? Long-standing controversy over the scientific use of the term ‘heavy metals’–proposal of a comprehensive definition. Toxicol. Environ. Chem.100(1), 6–19. 10.1080/02772248.2017.1413652 (2018).
-
- Oyugi, A. M., Kibet, J. K. & Adongo, J. O. A review of the health implications of heavy metals and pesticide residues on Khat users. Biol. Trace Elem. Res.45, 1–22. 10.1186/s42269-021-00613-y (2021).
-
- Kumar, M., Singh, S., Jain, A., Yadav, S., Dubey, A., Trivedi, S. P. (2024). A review on heavy metal-induced toxicity in fishes: Bioaccumulation, antioxidant defense system, histopathological manifestations, and transcriptional profiling of genes. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 83,127377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2023.127377 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

