Pan-cancer analysis reveals that TK1 promotes tumor progression by mediating cell proliferation and Th2 cell polarization
- PMID: 39343871
- PMCID: PMC11440694
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-024-03515-x
Pan-cancer analysis reveals that TK1 promotes tumor progression by mediating cell proliferation and Th2 cell polarization
Abstract
Background: TK1 (Thymidine kinase 1) is a member of the thymidine kinase family and has been observed to be significantly upregulated in a variety of cancer types. However, the exact roles of TK1 in tumor progression and the tumor immune microenvironment are not fully understood. This study aims to investigate the comprehensive involvement of TK1 in pan-cancer through the utilization of bioinformatics analysis, validation of pathological tissue samples, and in vitro experimental investigations.
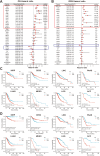
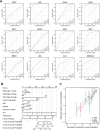
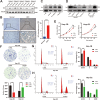
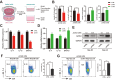
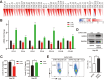
Methods: The expression profiles together with diagnostic and prognostic role of TK1 in pan-cancer were investigated though TCGA, TARGET, GTEx, and CPTAC databases. The single-sample gene set enrichment analysis (ssGSEA) and single-cell sequencing datasets were used to examine the relationship between TK1 and immune infiltration. The expression of TK1 were verified in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) through qPCR, western blotting and immunohistochemical assays. The proliferative capacity of HCC cell lines was assessed through CCK-8 and colony formation assays, while cytokine levels were measured via ELISA. Furthermore, flow cytometry was utilized to analyze cell cycle distribution and the proportions of Th2 cells.
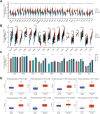
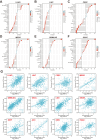
Results: TK1 was overexpressed in most cancers and demonstrated significant diagnostic and prognostic value. Among the various immune cells in pan-cancer, Th2 cells exhibited the closest association with TK1. Furthermore, the single-cell atlas provided insights into the distribution and proportion of TK1 in immune cells of HCC. In vitro experiments revealed an elevated expression of TK1 in HCC tissue and cell lines, and its role in influencing HCC cell proliferation by regulating G0/G1 phase arrest. Additionally, TK1 in cancer cells was found to potentially modulate Th2 cell polarization through the chemokine CCL5.
Conclusion: TK1 holds immense potential as a biomarker for pan-cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Additionally, targeting the expression of TK1 represents a promising therapeutic approach that can enhance the efficacy of current anti-tumor immunotherapy by modulating Th2 cell polarization and multiple mechanisms.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; Pan-cancer; TK1; Th2 CD4+ T cells; Tumor immune microenvironment.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

