CircRNA and lncRNA-encoded peptide in diseases, an update review
- PMID: 39343883
- PMCID: PMC11441268
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-024-02131-7
CircRNA and lncRNA-encoded peptide in diseases, an update review
Abstract
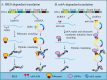
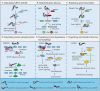
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), including circular RNAs (circRNAs) and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), are unique RNA molecules widely identified in the eukaryotic genome. Their dysregulation has been discovered and played key roles in the pathogenesis of numerous diseases, including various cancers. Previously considered devoid of protein-coding ability, recent research has revealed that a small number of open reading frames (ORFs) within these ncRNAs endow them with the potential for protein coding. These ncRNAs-derived peptides or proteins have been proven to regulate various physiological and pathological processes through diverse mechanisms. Their emerging roles in disease diagnosis and targeted therapy underscore their potential utility in clinical settings. This comprehensive review aims to provide a systematic overview of proteins or peptides encoded by lncRNAs and circRNAs, elucidate their production and functional mechanisms, and explore their promising applications in cancer diagnosis, disease prediction, and targeted therapy.
Keywords: Diagnosis; Molecular mechanisms; Non-coding RNAs; Peptide encoding; Targeted therapy; Tumorigenesis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

